Deploy CodeGen Application on AMD EPYC™ Processors with Docker Compose¶
This README outlines the process for deploying the CodeGen application using Docker Compose on a system equipped with AMD EPYC™ Processors. It provides detailed instructions to configure, run, and validate the services, with the default configuration using the vLLM backend for LLM serving.
Table of Contents¶
Overview¶
This guide focuses on running the pre-configured CodeGen service using Docker Compose on AMD EPYC CPUs.
Prerequisites¶
Docker and Docker Compose installed.
AMD EPYC CPU.
Git installed (for cloning repository).
Hugging Face Hub API Token (for downloading models).
Access to the internet (or a private model cache).
Clone the
GenAIExamplesrepository:git clone https://github.com/opea-project/GenAIExamples.git cd GenAIExamples/CodeGen/docker_compose
Quick Start Deployment¶
Install Docker: Ensure Docker is installed on your system. If Docker is not already installed, use the provided script to set it up:
source ./install_docker.sh
This script installs Docker and its dependencies. After running it, verify the installation by checking the Docker version:
docker --version
If Docker is already installed, this step can be skipped.
Configure Environment:
Set required environment variables in your shell:i) Determine your host’s external IP address:
Run the following command in your terminal to list network interfaces:ifconfig
Look for the inet address associated with your active network interface (e.g., enp99s0). For example:
enp99s0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 inet 10.101.16.119 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 10.101.16.255
In this example, the (
host_ip) would be (10.101.16.119).# Replace with your host's external IP address export host_ip="your_external_ip_address"
ii) Generate a HuggingFace Access Token:
Some HuggingFace resources, such as some models, are only accessible if you have an access token. If you do not already have a HuggingFace access token, you can create one by first creating an account by following the steps provided at HuggingFace and then generating a user access token.# Replace with your Hugging Face Hub API token export HF_TOKEN="your_huggingface_token"
iii) Set environment variables:
The model_cache directory, by default, stores models in the ./data directory. To change this, use the following command:# Optional export model_cache=/home/documentation/data_codegen/data # Path to save cache models
Optional: Configure proxy settings if needed:
# export http_proxy="your_http_proxy" # export https_proxy="your_https_proxy" # export no_proxy="localhost,127.0.0.1,${host_ip}" # Add other hosts if necessaryTo set other environment variables:
cd amd/cpu/epyc source ./set_env.sh
For instance, edit the set_env.sh to change the LLM model
export LLM_MODEL_ID="Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-7B-Instruct"
can be changed to other model if needed
export LLM_MODEL_ID="Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct"
Start Services (vLLM Profile):
docker compose --profile codegen-epyc-vllm up -d
Validate: Wait several minutes for models to download (especially the first time) and services to initialize. Check container logs (
docker compose logs -f <service_name>) or proceed to the validation steps below.
Available Deployment Options¶
The compose.yaml file uses Docker Compose profiles to select the LLM serving backend.
Default: vLLM-based Deployment (--profile codegen-epyc-vllm)¶
Profile:
codegen-epyc-vllmDescription: Uses vLLM as the LLM serving engine. This is the default profile used in the Quick Start.
Services Deployed:
codegen-vllm-server,codegen-llm-server,codegen-tei-embedding-server,codegen-retriever-server,redis-vector-db,codegen-dataprep-server,codegen-backend-server,codegen-gradio-ui-server.To Run:
# Ensure environment variables (host_ip, HF_TOKEN) are set docker compose --profile codegen-epyc-vllm up -d
TGI-based Deployment (--profile codegen-epyc-tgi)¶
Profile:
codegen-epyc-tgiDescription: Uses Hugging Face Text Generation Inference (TGI) as the LLM serving engine.
Services Deployed:
codegen-tgi-server,codegen-llm-server,codegen-tei-embedding-server,codegen-retriever-server,redis-vector-db,codegen-dataprep-server,codegen-backend-server,codegen-gradio-ui-server.To Run:
# Ensure environment variables (host_ip, HF_TOKEN) are set docker compose --profile codegen-epyc-tgi up -d
Compose Profiles¶
Docker Compose profiles (codegen-epyc-vllm, codegen-epyc-tgi) determine which LLM serving backend (vLLM or TGI) and its associated dependencies are started. Typically, only one profile should be active at a time.
Building Custom Images (Optional)¶
If you need to modify the microservices:
Clone the OPEA GenAIComps repository.
Follow build instructions in the respective component directories (e.g.,
comps/llms/text-generation,comps/codegen,comps/ui/gradio, etc.). Use the provided Dockerfiles (e.g.,CodeGen/Dockerfile,CodeGen/ui/docker/Dockerfile.gradio).Tag your custom images appropriately (e.g.,
my-custom-codegen:latest).Update the
image:fields in thecompose.yamlfile to use your custom image tags.
Refer to the main CodeGen README for links to relevant GenAIComps components.
Validate Services¶
Check Container Status¶
Ensure all containers associated with the chosen profile are running:
docker compose --profile <profile_name> ps
# Example: docker compose --profile codegen-epyc-vllm ps
Check logs for specific services: docker compose logs <service_name>
Run Validation Script/Commands¶
Use curl commands to test the main service endpoints. Ensure host_ip is correctly set in your environment.
Validate LLM Serving Endpoint (Example for vLLM on default port 9000 internally, exposed differently):
# This command structure targets the OpenAI-compatible vLLM endpoint curl http://${host_ip}:9000/v1/chat/completions \ -X POST \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ -d '{"model": "Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-7B-Instruct", "messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Implement a basic Python class"}], "max_tokens":32}'
Expected Output: A JSON response with generated code in
choices[0].message.content.
Validate CodeGen Gateway (MegaService on default port 7778):
curl http://${host_ip}:7778/v1/codegen \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{"messages": "Write a Python function that adds two numbers."}'
Expected Output: A stream of JSON data chunks containing generated code, ending with
data: [DONE].
Accessing the User Interface (UI)¶
Multiple UI options can be configured via the compose.yaml.
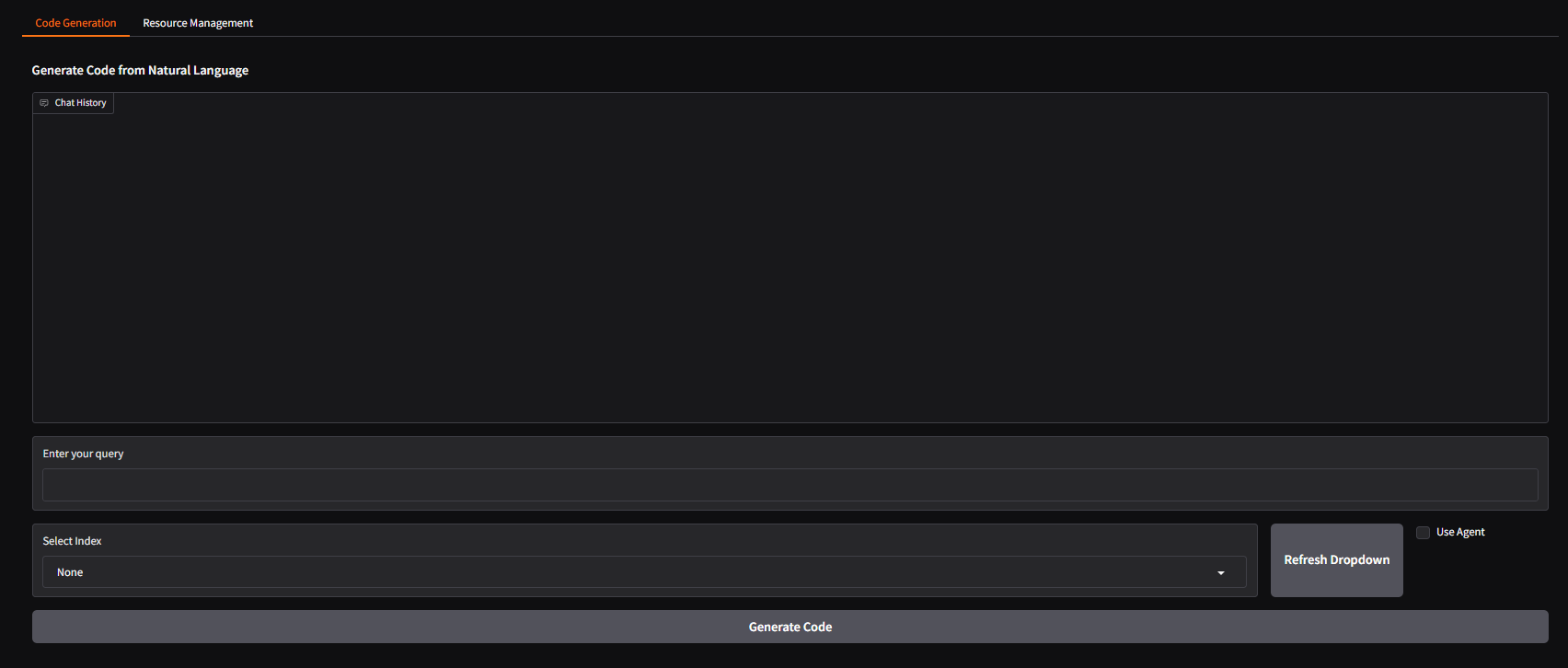
Gradio UI (Default)¶
Access the default Gradio UI by navigating to:
http://{host_ip}:5173
(Port 5173 is the default host mapping for codegen-gradio-ui-server)
Svelte UI (Optional)¶
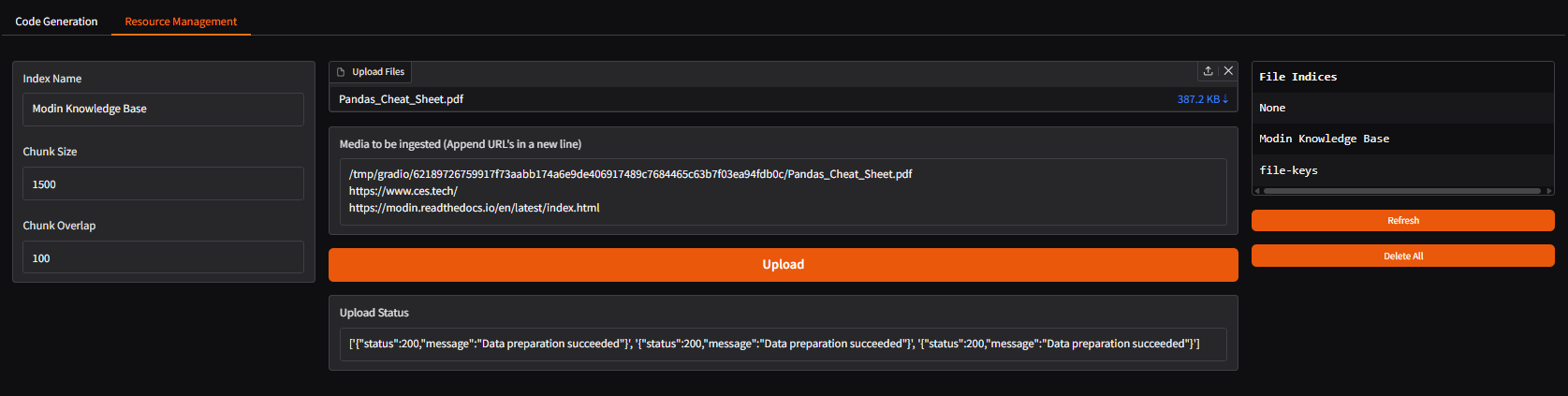
Modify
compose.yaml: Comment out thecodegen-gradio-ui-serverservice and uncomment/add thecodegen-epyc-ui-server(Svelte) service definition, ensuring the port mapping is correct (e.g.,"- 5173:5173").Restart Docker Compose:
docker compose --profile <profile_name> up -dAccess:
http://{host_ip}:5173(or the host port you mapped).
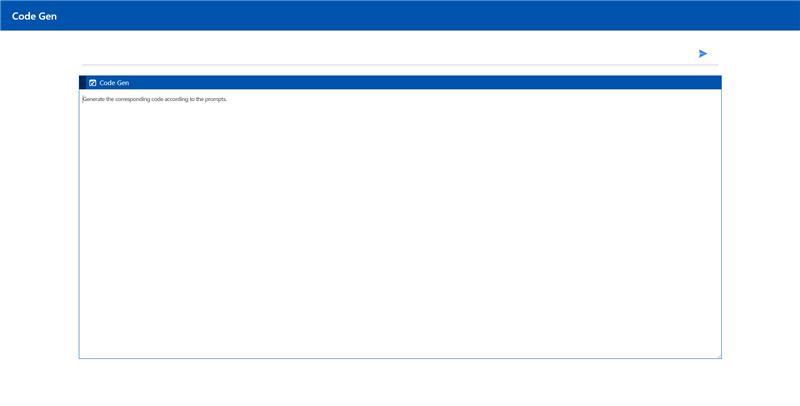
React UI (Optional)¶
Modify
compose.yaml: Comment out the default UI service and uncomment/add thecodegen-epyc-react-ui-serverdefinition, ensuring correct port mapping (e.g.,"- 5174:80").Restart Docker Compose:
docker compose --profile <profile_name> up -dAccess:
http://{host_ip}:5174(or the host port you mapped).
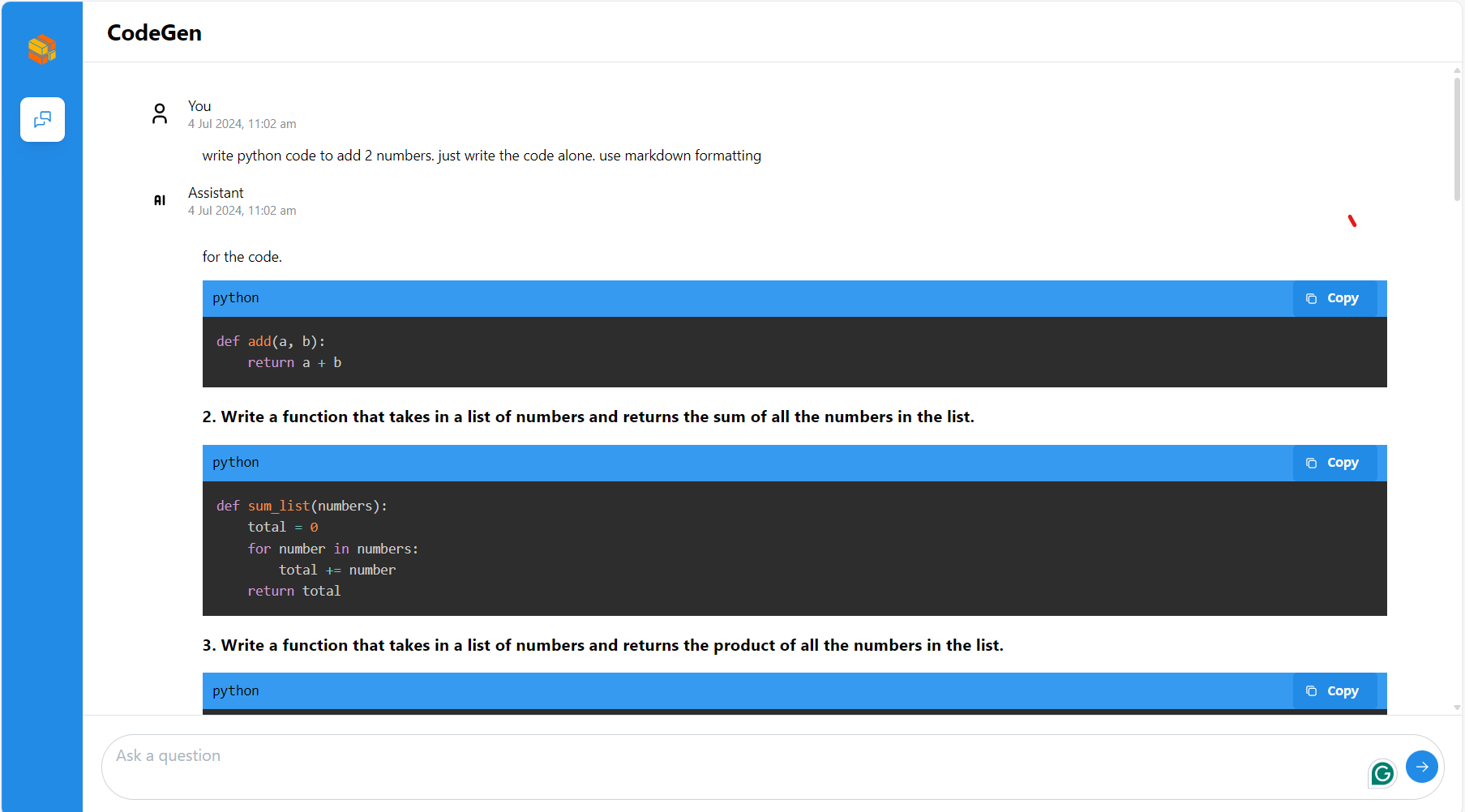
VS Code Extension (Optional)¶
Users can interact with the backend service using the Neural Copilot VS Code extension.
Install: Find and install
Neural Copilotfrom the VS Code Marketplace.
Configure: Set the “Service URL” in the extension settings to your CodeGen backend endpoint:
http://${host_ip}:7778/v1/codegen(use the correct port if changed).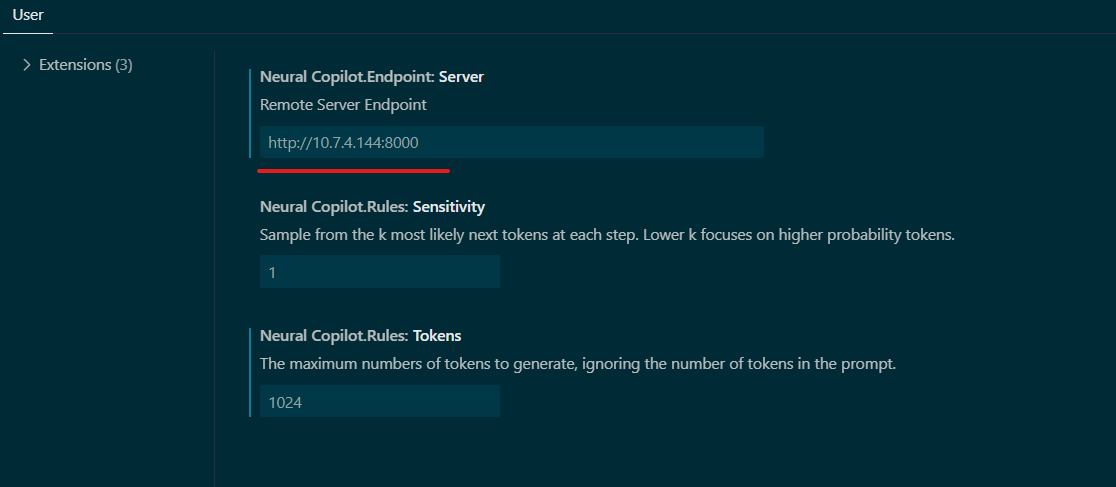
Usage:
Inline Suggestion: Type a comment describing the code you want (e.g.,
# Python function to read a file) and wait for suggestions.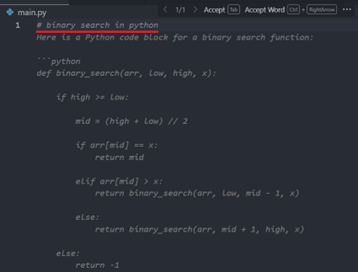
Chat: Use the Neural Copilot panel to chat with the AI assistant about code.
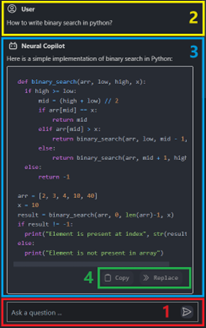
Troubleshooting¶
Model Download Issues: Check
HF_TOKEN. Ensure internet connectivity or correct proxy settings. Check logs oftgi-service/vllm-serviceandtei-embedding-server. Gated models need prior Hugging Face access.Connection Errors: Verify
host_ipis correct and accessible. Checkdocker psfor port mappings. Ensureno_proxyincludeshost_ipif using a proxy. Check logs of the service failing to connect (e.g.,codegen-backend-serverlogs if it can’t reachcodegen-llm-server).“Container name is in use”: Stop existing containers (
docker compose down) or changecontainer_nameincompose.yaml.Resource Issues: CodeGen models can be memory-intensive. Monitor host RAM usage. Increase Docker resources if needed.
Stopping the Application¶
docker compose --profile <profile_name> down
# Example: docker compose --profile codegen-epyc-vllm down
Next Steps¶
Consult the OPEA GenAIComps repository for details on individual microservices.
Refer to the main CodeGen README for links to benchmarking and Kubernetes deployment options.
Profile Microservices¶
To further analyze MicroService Performance, users could follow the instructions to profile MicroServices.
1. vLLM backend Service¶
Users could follow previous section to testing vLLM microservice or CodeGen MegaService. By default, vLLM profiling is not enabled. Users could start and stop profiling by following commands.
Start vLLM profiling¶
curl http://${host_ip}:8028/start_profile \
-X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"model": "Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-7B-Instruct"}'
After vLLM profiling is started, users could start asking questions and get responses from vLLM MicroService
curl http://${host_ip}:8028/v1/chat/completions \
-X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"model": "Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-7B-Instruct", "messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Write a C Program to add two numbers"}], "max_tokens":32}'
Stop vLLM profiling¶
By following command, users could stop vLLM profiling and generate a *.pt.trace.json.gz file as profiling result under /mnt folder in vllm-server docker instance.
curl http://${host_ip}:8028/stop_profile \
-X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"model": "Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-7B-Instruct"}'
After vllm profiling is stopped, users could use below command to get the *.pt.trace.json.gz file under /mnt folder.
docker cp vllm-server:/mnt/ .
Check profiling result¶
Open a web browser and type “chrome://tracing” or “ui.perfetto.dev”, and then load the json.gz file.
Conclusion¶
This guide should enable developer to deploy the default configuration or any of the other compose yaml files for different configurations. It also highlights the configurable parameters that can be set before deployment.