🚀 RAG Pilot - A RAG Pipeline Tuning Tool¶
📖 Overview¶
RAG Pilot provides a set of tuners to optimize various parameters in a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) pipeline. Each tuner allows fine-grained control over key aspects of parsing, chunking, postporcessing, and generating selection, enabling better retrieval and response generation.
🧠 Available Tuners¶
Tuner |
Stage |
Function |
Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|
EmbeddingModelTuner |
Retrieval |
Tune embedding model and related parameters |
Allows selection and configuration of the embedding model used for vectorization, including model name and optional parameters like dimension or backend. |
NodeParserTuner |
Retrieval |
Tune |
Configures chunking behavior for document parsing by adjusting the size of individual text chunks and their overlap to ensure context retention. |
RetrievalTopkTuner |
Retrieval |
Tune |
Adjusts how many documents are retrieved before reranking, balancing recall and performance. |
RerankerTopnTuner |
Postprocessing |
Tune |
Adjusts the number of top-ranked documents returned after reranking, optimizing relevance and conciseness. |
PromptTuner |
Generator |
Tune |
Generate multiple responses using different prompts for users. |
These tuners help in optimizing document parsing, chunking strategies, reranking efficiency, and embedding selection for improved RAG performance.
🚦 How to use RAG Pilot¶
▶️ Use RAG Pilot with UI¶
RAG Pilot provides an interactive UI interface to assist with usage, including the following stages:
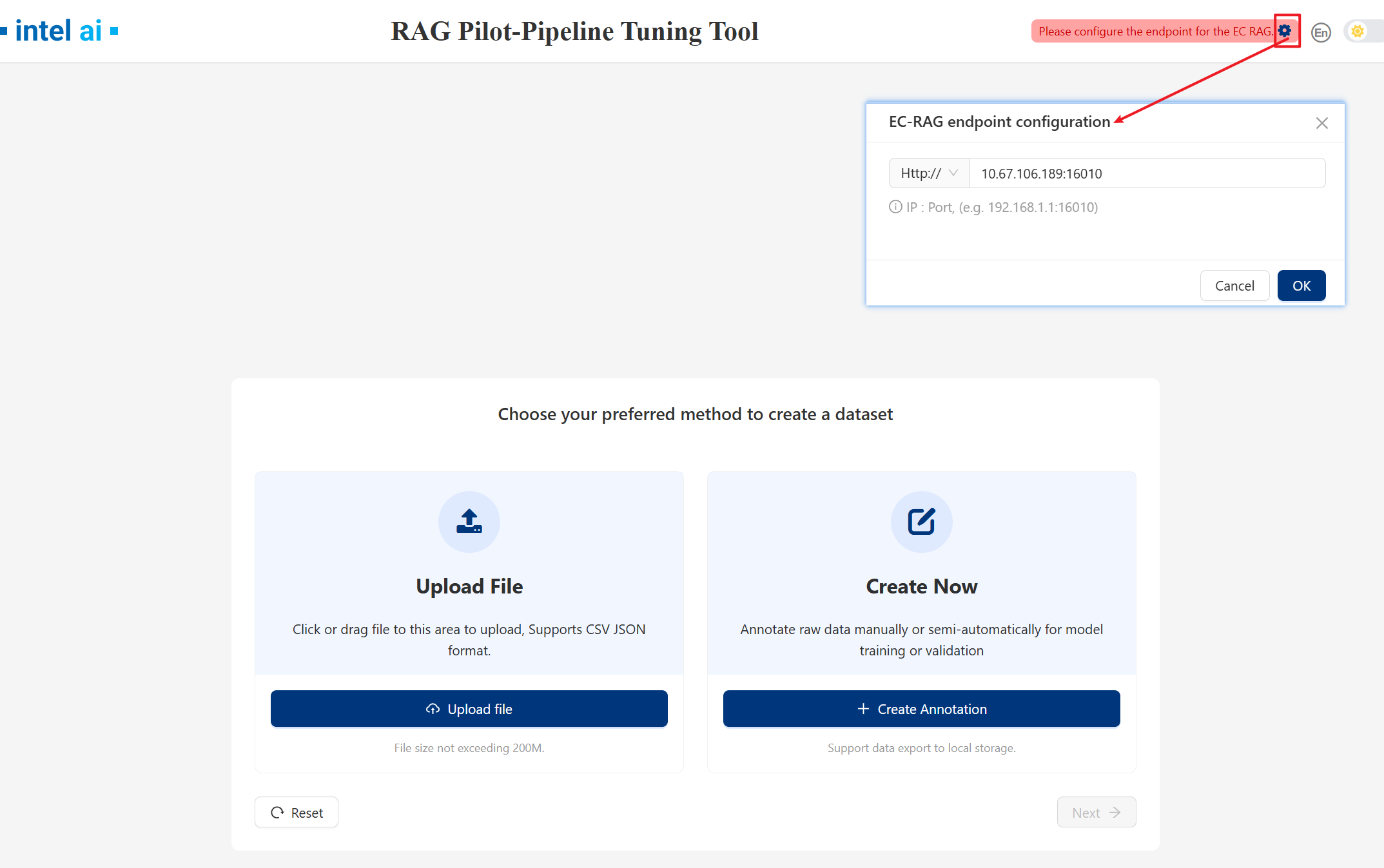
1. Set EC-RAG endpoint¶
Click the gear button to set EC-RAG endpoint:
2. Ground truth upload¶
We provide two ways to upload Ground truth:
Upload File and Create New
First time you use Rag Pilot you can start with Create Now.
2.1 Create Now¶
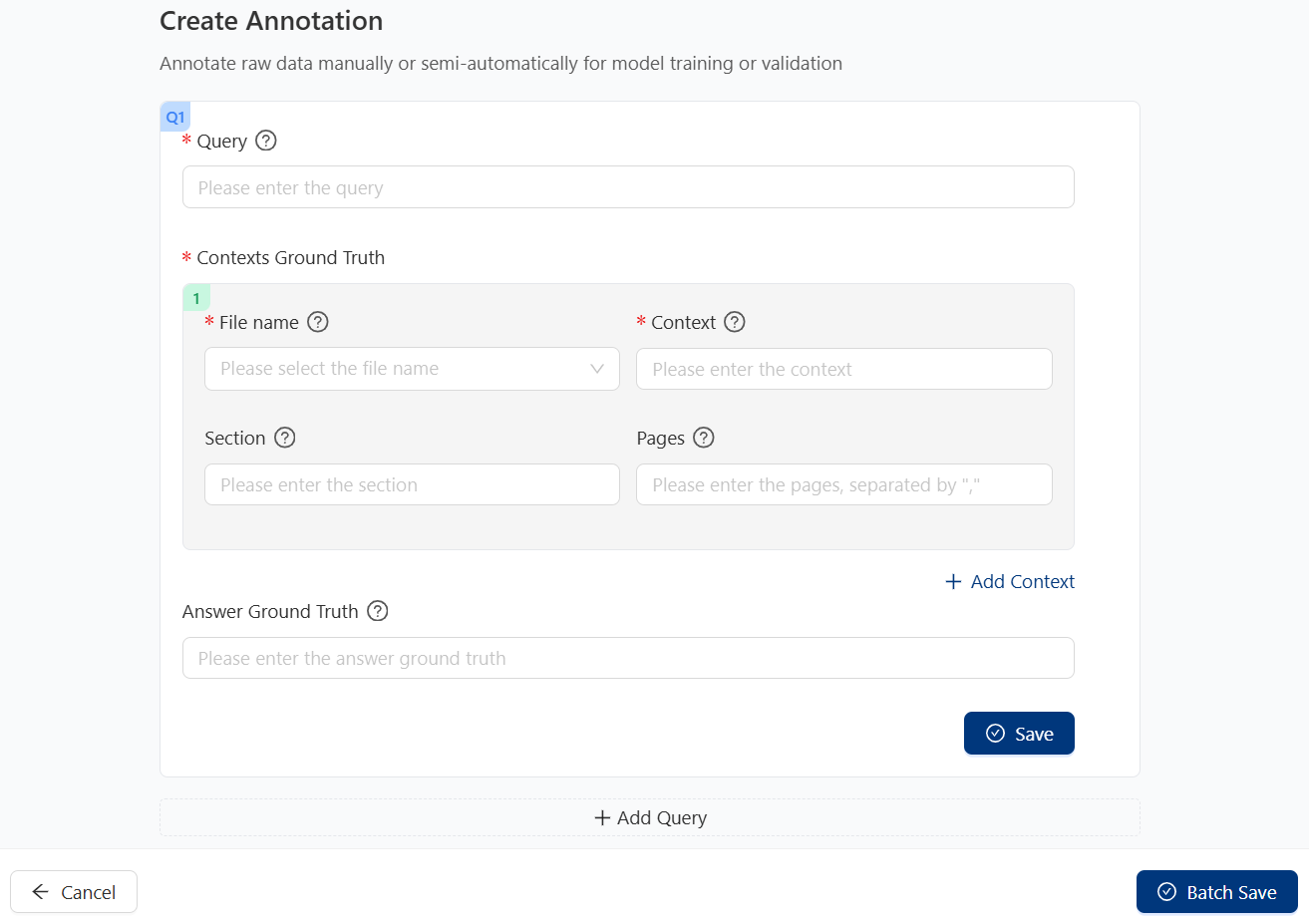
Available options and meanings:
Item
usage
Query
The query you want to ask.
File name
File name which containing the context, select from the drop-down menu.
Context
Context ground truth which related to the query.
Section
Node with context in the file.
Pages
The page number of the context in the file.
Add Context: Add context of the same query.Add Query: Add other queries infornation.Save: Save single query ground truth information.Batch Save: Save all queries ground truth information.Once the user click
SaveorBatch Savebutton ,RAG Pilot will search matched nodes based on the ground truth information you entered as ground truth. If no matched node, RAG Pilot will will return the top few nodes with the highest match scores for the user to select: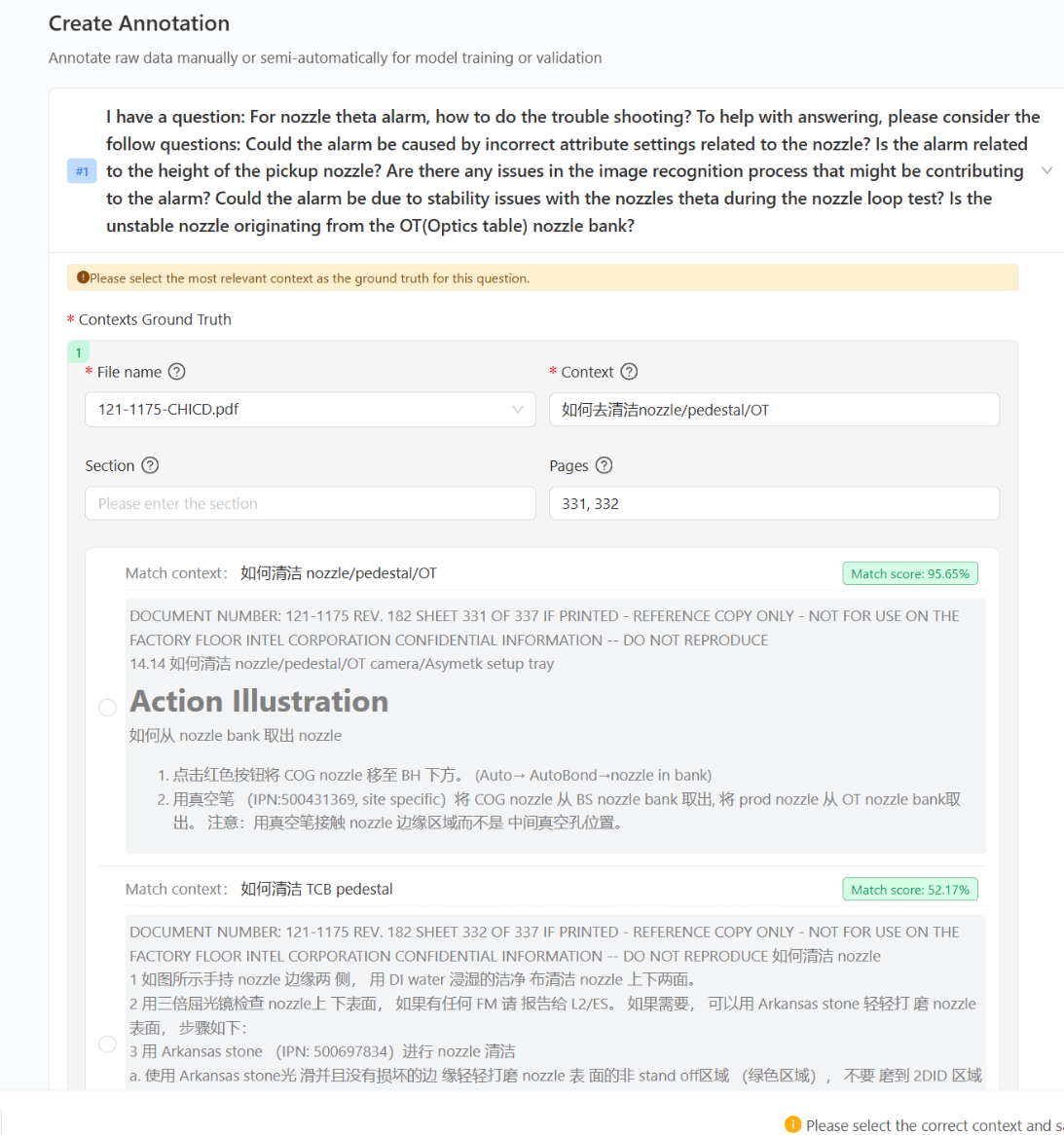
After create gt, you can click
downloadbutton to download ground truth file forUpload Files.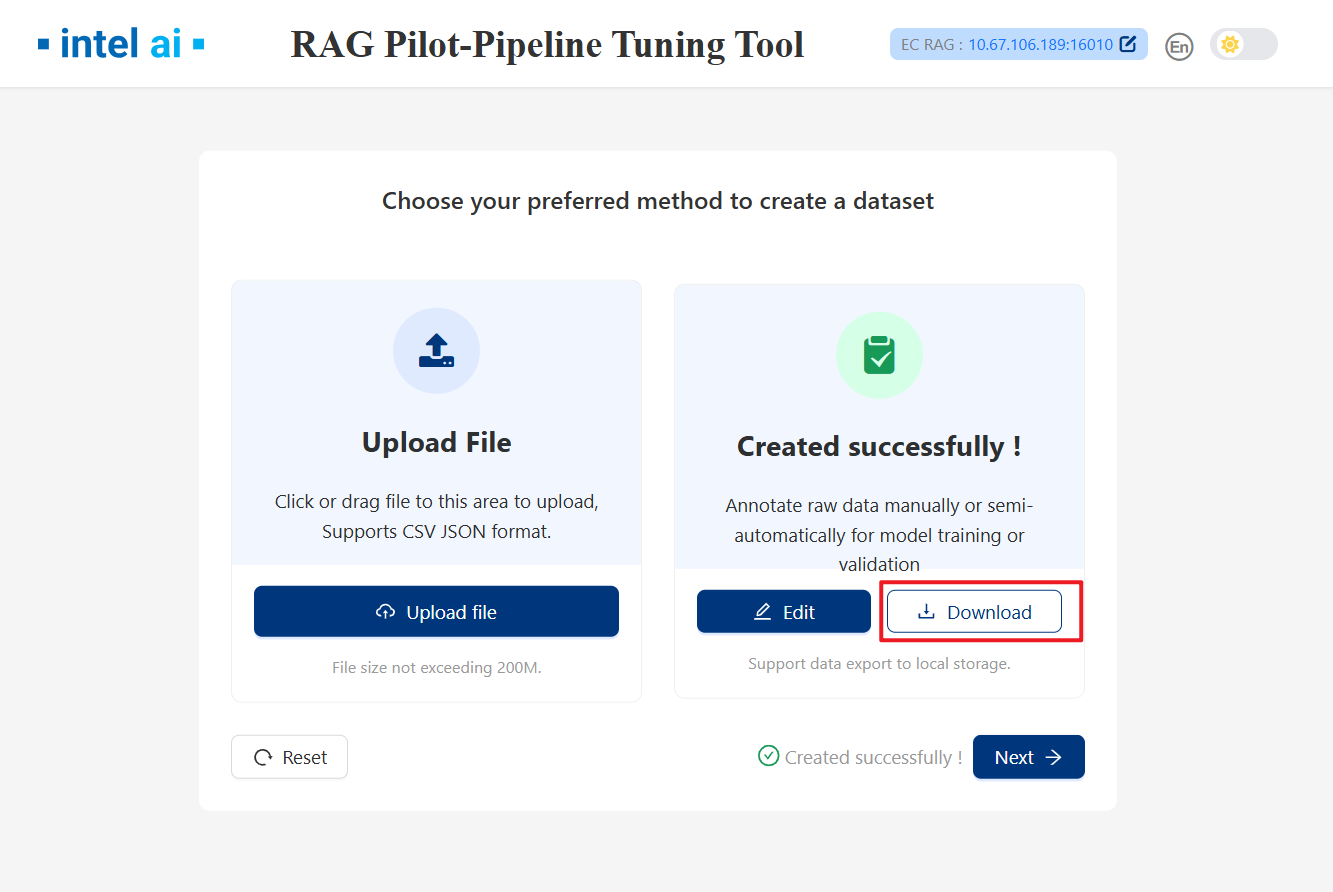
2.2 Upload files¶
After create gt, you can use downloaded json file as upload file.
3. Response Rating¶
After groud truth loading, RAG Pilot wii generate response bases on EC-RAG current pipeline.
Click
Runto get rating results.Click
Skipto skip rating.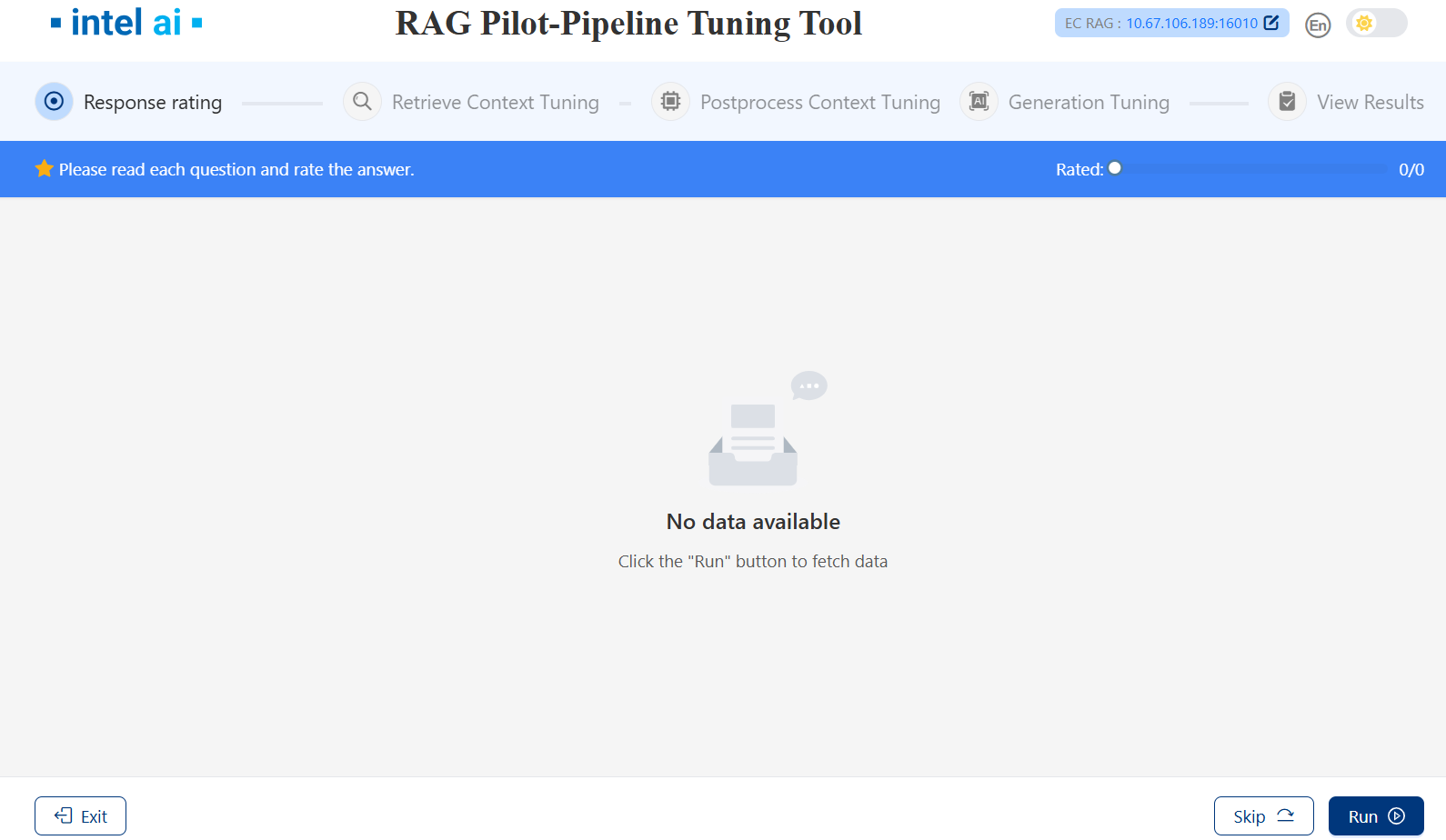
After clicking Run:
You can rating each result after the responses generated.
Click numbers on the left to switch between responses of different queries.
Click
Nextto the next stage.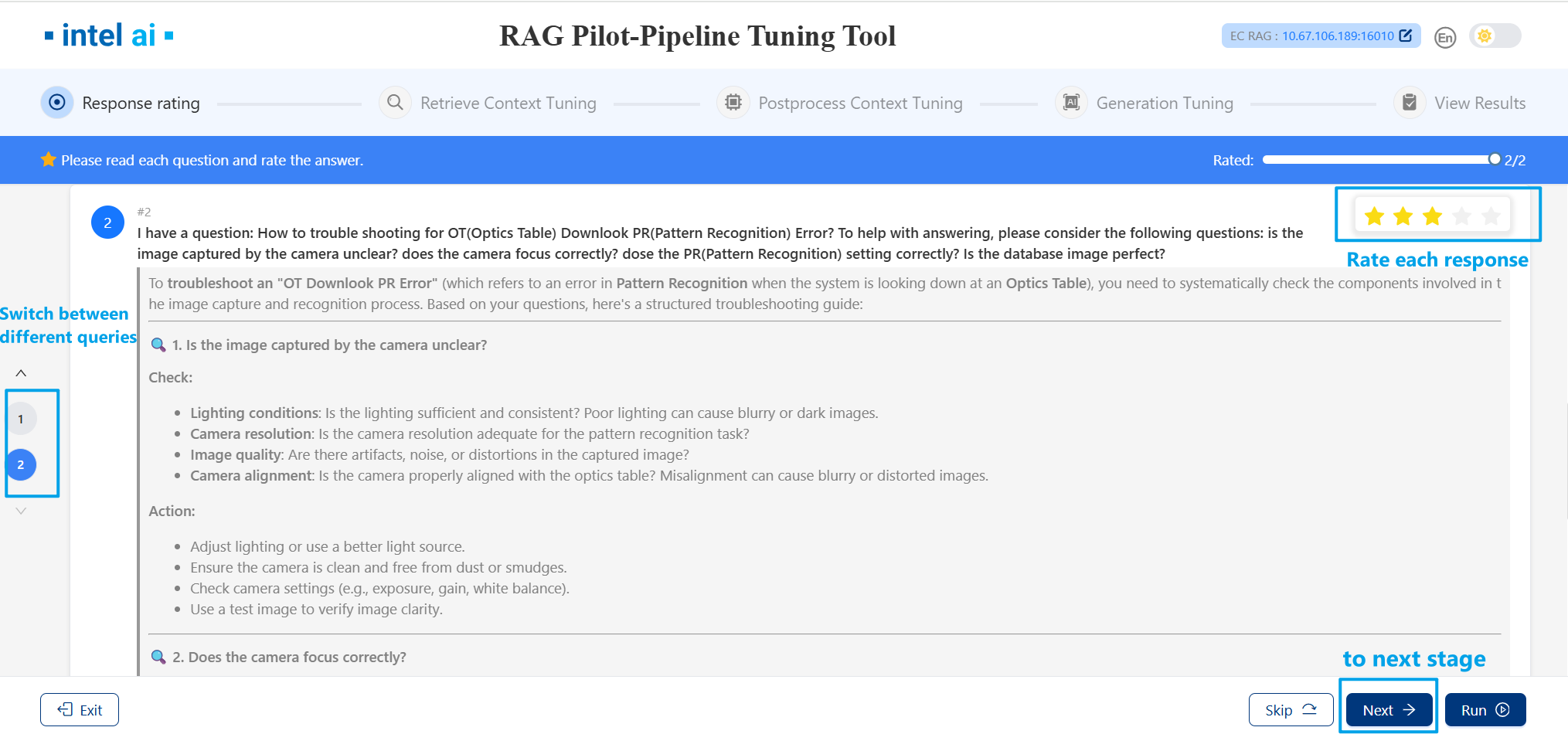
4. Retrieve Context Tuning¶
During this stage, RAG Pilot will execute four tuners:ObserberTuner, EmbeddingModelTuner, NodeParserTuner and RetrievalTopKTuner.
4.1 Retrieve Context Tuning Configure¶
You can configure the specific content for each tuners.
Click
Run Tunerswill start retrieval stage tuning.Click
Cancelthen clickSkipto skip the Retrieve Context Tuning stage.Support exporting and importing tuners configure with
ExportandImportbuttons.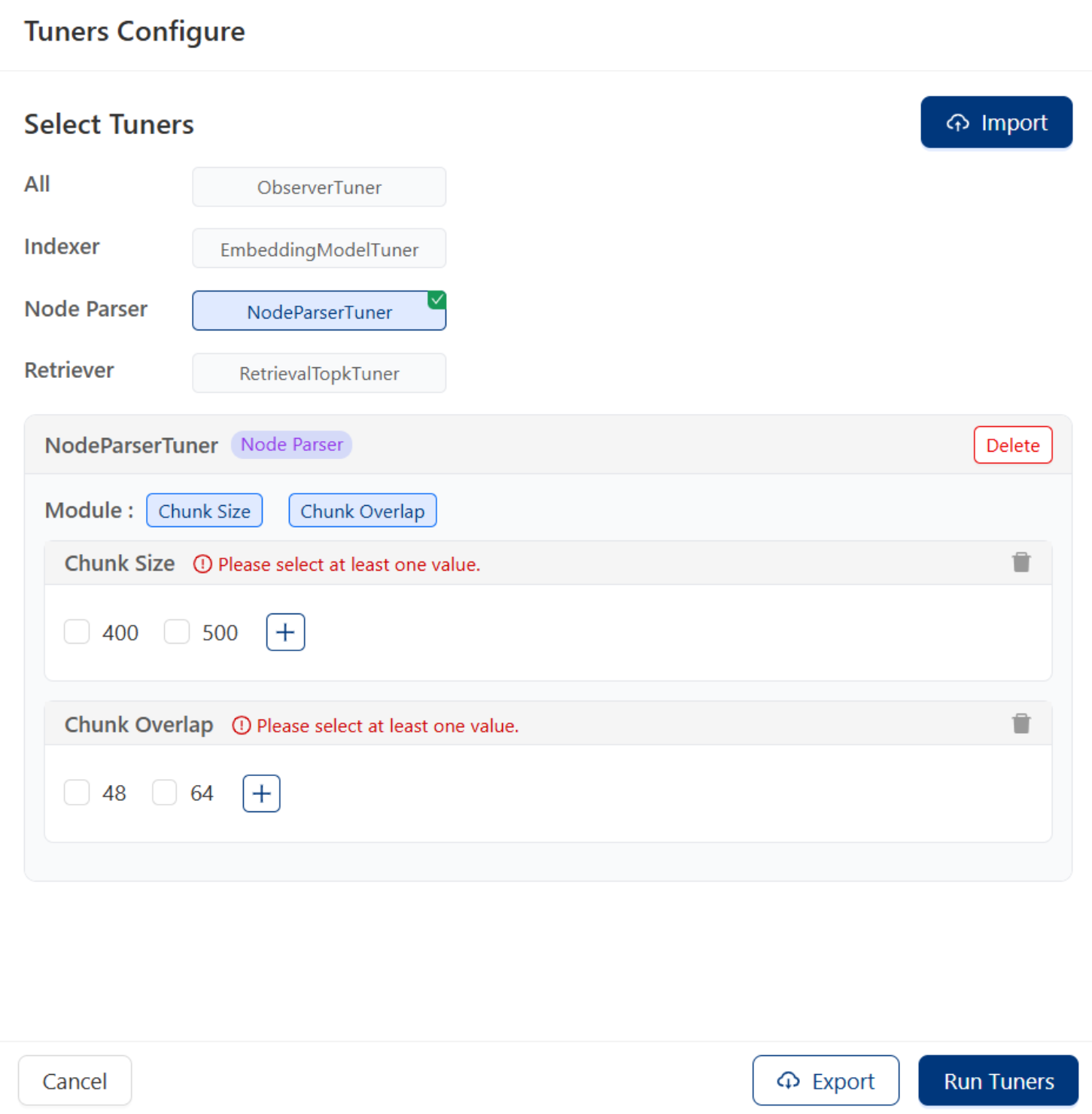
4.2 Retrieve Context Tuning Run & Results¶
After clicking Run Tuners, these tuners will experiment with various parameter combinations to construct corresponding pipelines, ultimately selecting the most effective pipeline as the operational one.
Click numbers on the left to switch between different queries.
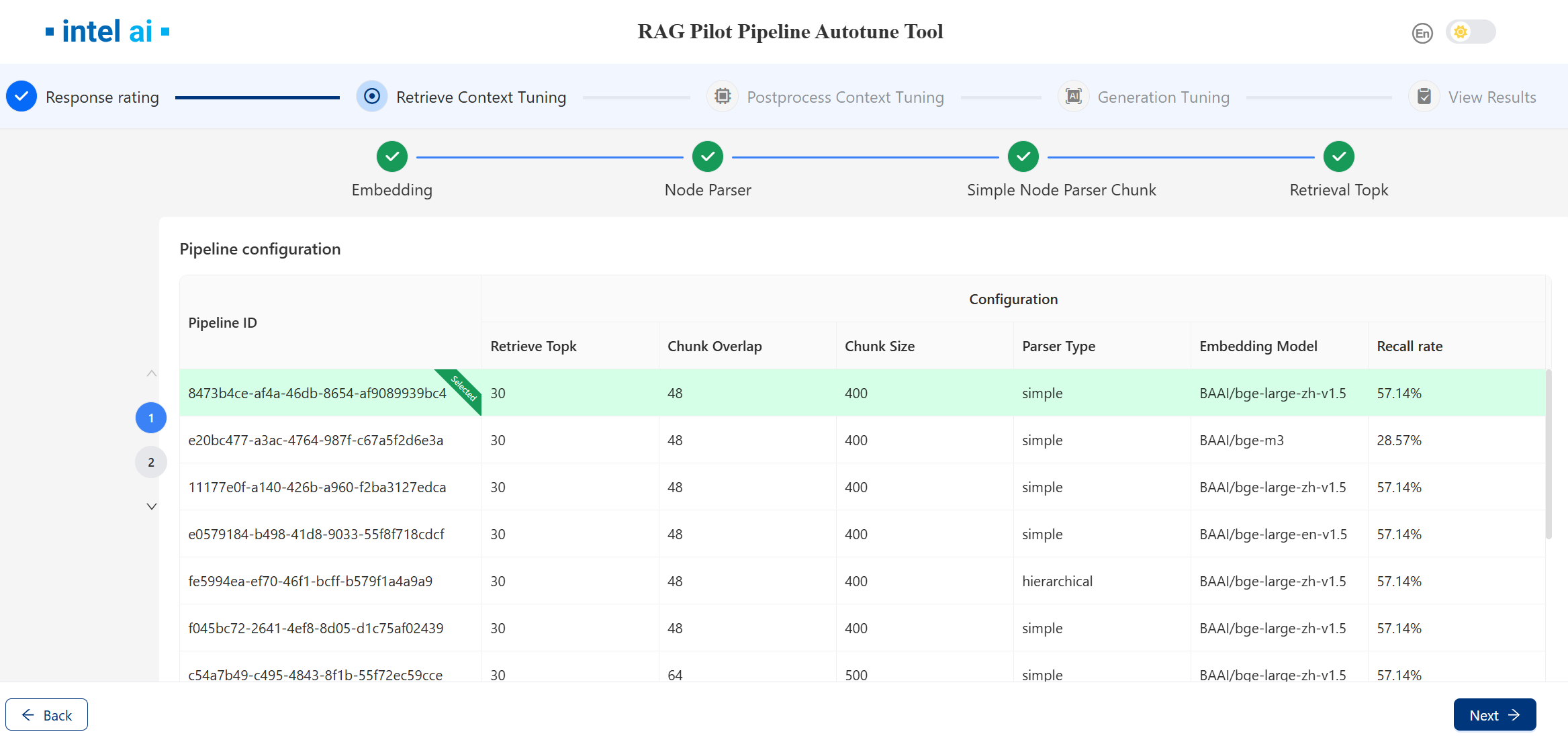
Once the selected tuners have completed their tasks, the page will display the results, including the
ground truth hitsand theretrieved chunks.Users can search text via the search box in the upper-right corner to observe which parts of the context match the ground truth context. Text entered into the search box will be highlighted.
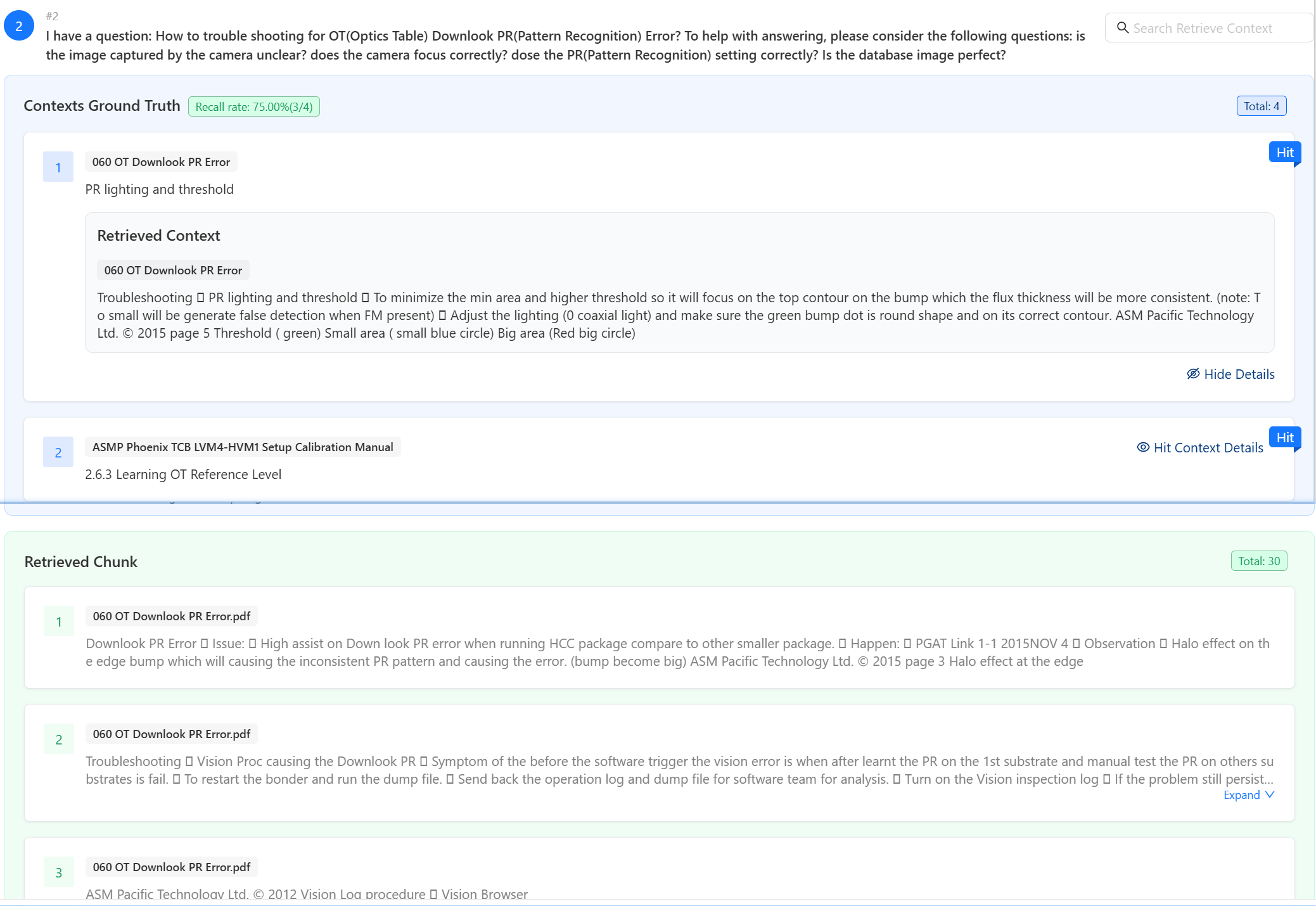
Click
Nextto the Postprocess Context Tuning stage.
5. Postprocess Context Tuning¶
This stage includes one tuner:RerankerTopnTuner which adjusts the number of top-ranked documents returned after reranking, optimizing relevance and conciseness.
5.1 Postprocess Context Tuning Configure¶
Users can configure RerankerTopnTuner with UI.
Click
Run Tunerswill start retrieval stage tuning.Click
Cancelthen clickSkipto skip the Postprocess Context Tuning.Support exporting and importing tuners configure with
ExportandImportbuttons.
5.2 Postprocess Context Tuning Run & Results¶
After the tuning finished, the page will show recall plots of different topn.
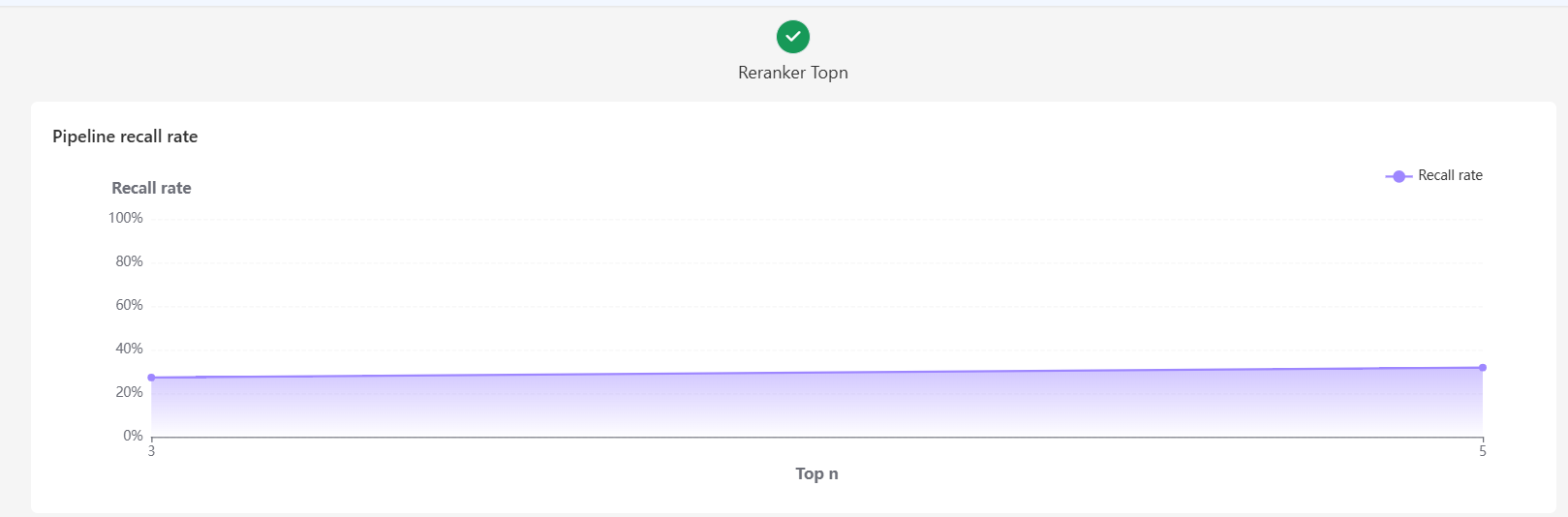
You can select the desired
Top nvalue.The page will display the
ground truth hitsfrom both the postprocessing and retrieval stages, as well as theretrieved chunksfrom the postprocessing stage.Click numbers on the left to switch between different queries.
Users can search text via the search box in the upper-right corner to observe which parts of the context match the ground truth context. Text entered into the search box will be highlighted.
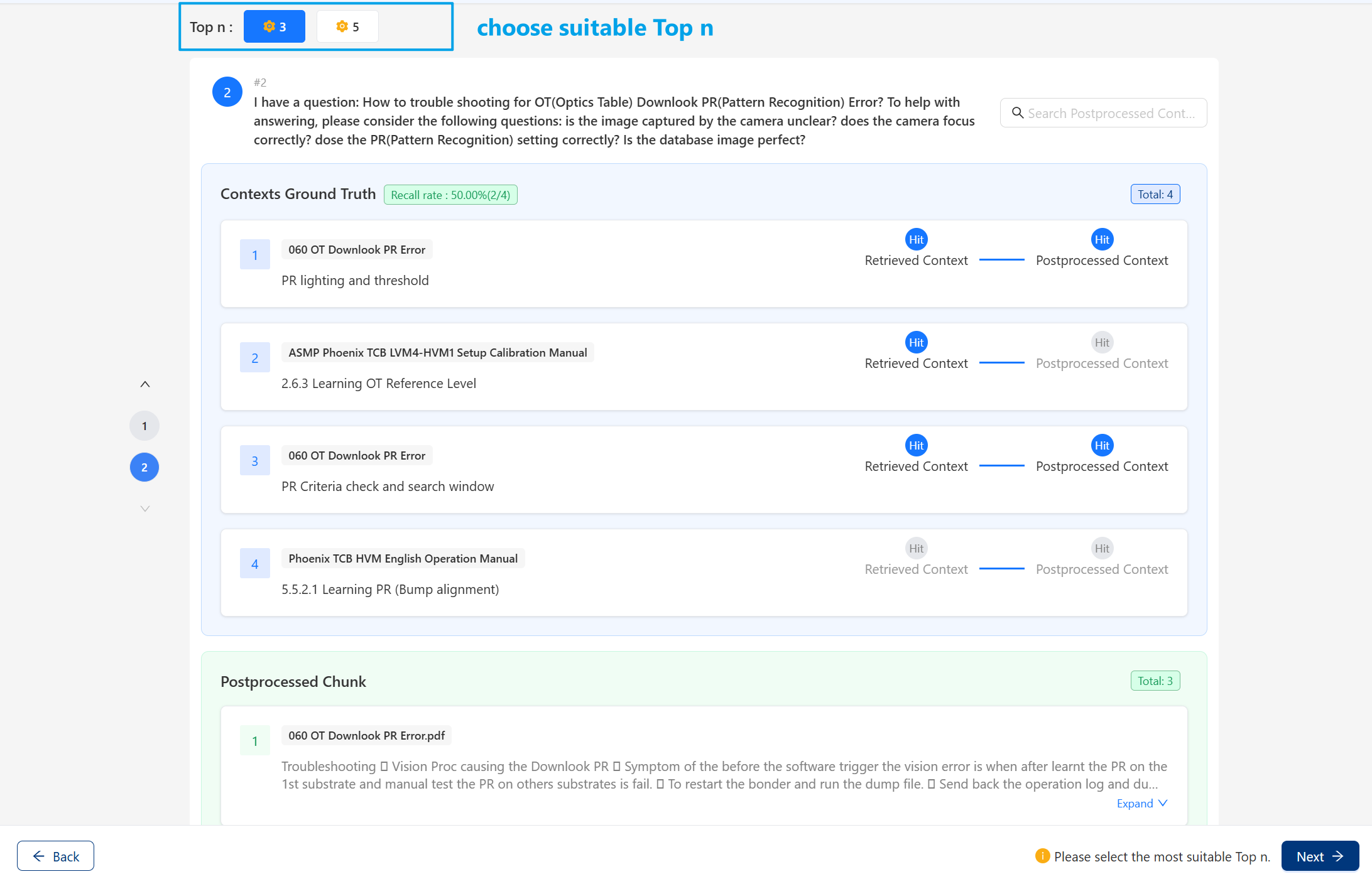
Click
Nextto the generation tuning stage.
6. Generation tuning¶
This stage includes one tuner: PromptTuner, you can add your own prompts to generate different responses.
6.1 Generation Tuning Configure¶
Users can configure PromptTuner with UI:
Click
Cancelthen clickSkipto skip the Generation Tuning.Support exporting and importing tuners configure with
ExportandImportbuttons.
Click
Run tunerswill display all activated prompts: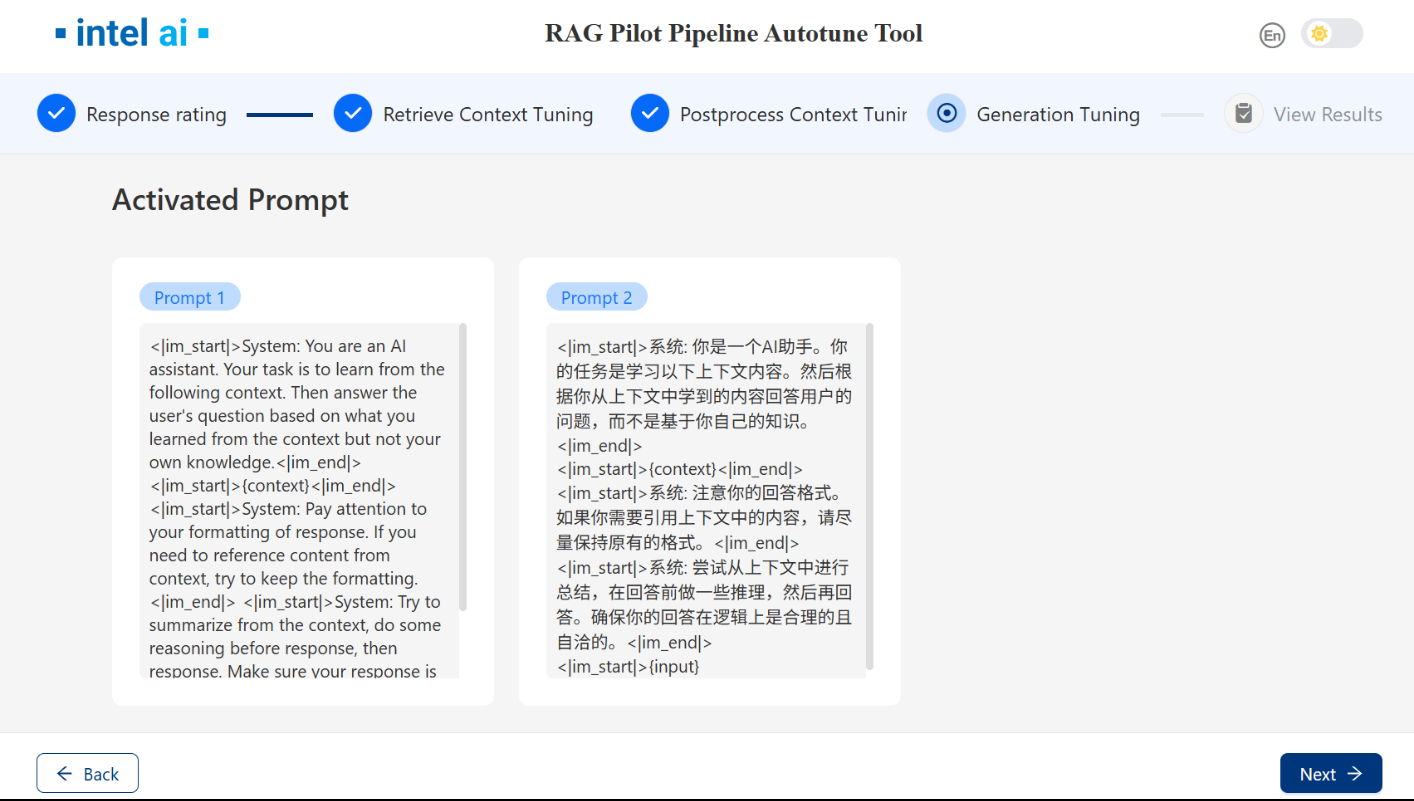
Click
Nextto utilize these prompts to generate answers.
6.2 Generation Tuning Run & Results¶
Once the response is generated, you can then evaluate and rate the responses generated from different prompts.
Click numbers on the left to switch between different queries.
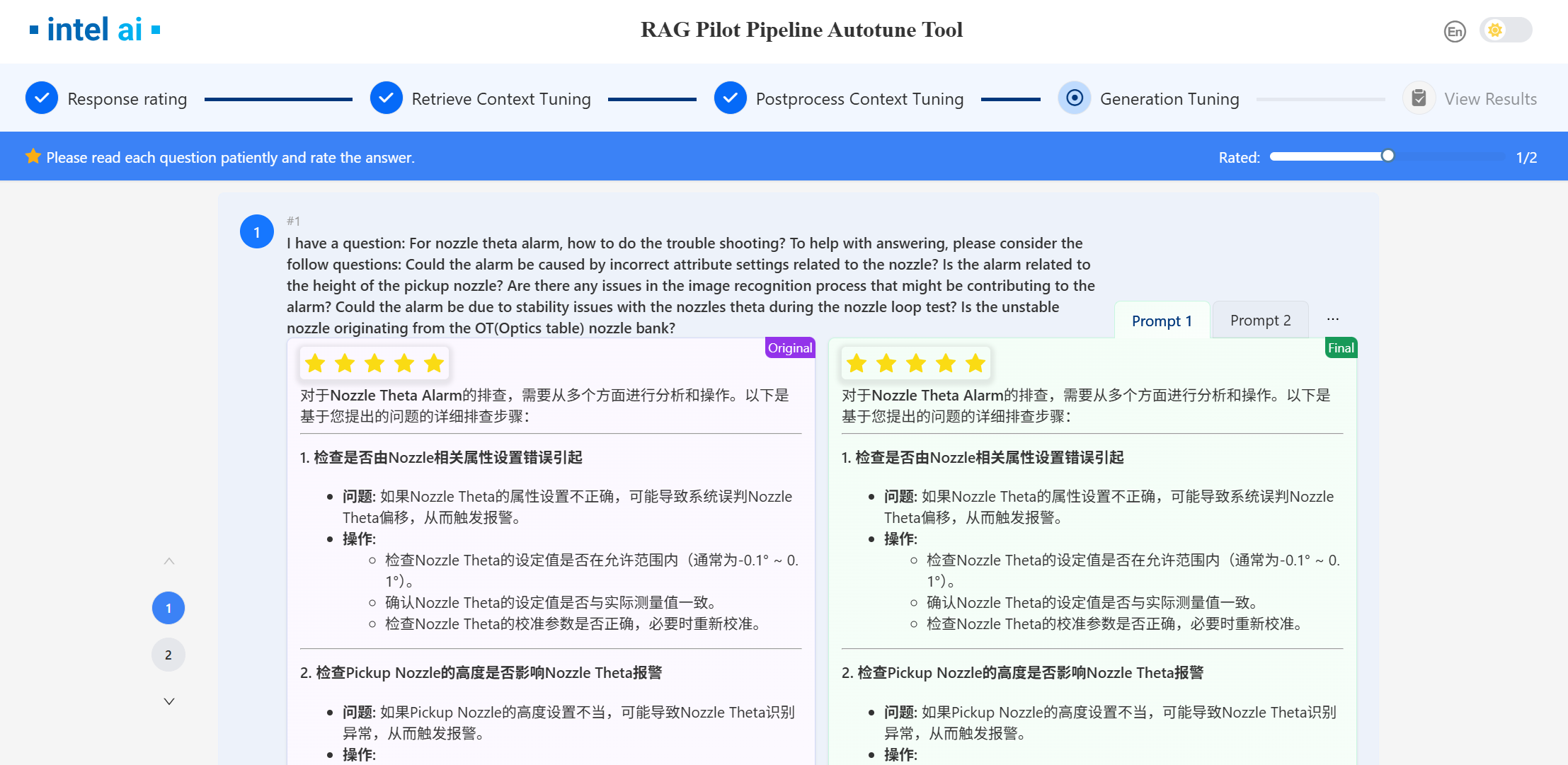
Click Next to the next stage.
7. View Results¶
After Generation tuning stage, you can see the overall rating of different prompts. For each pipeline, you can view configuration details and update them to EC-RAG.
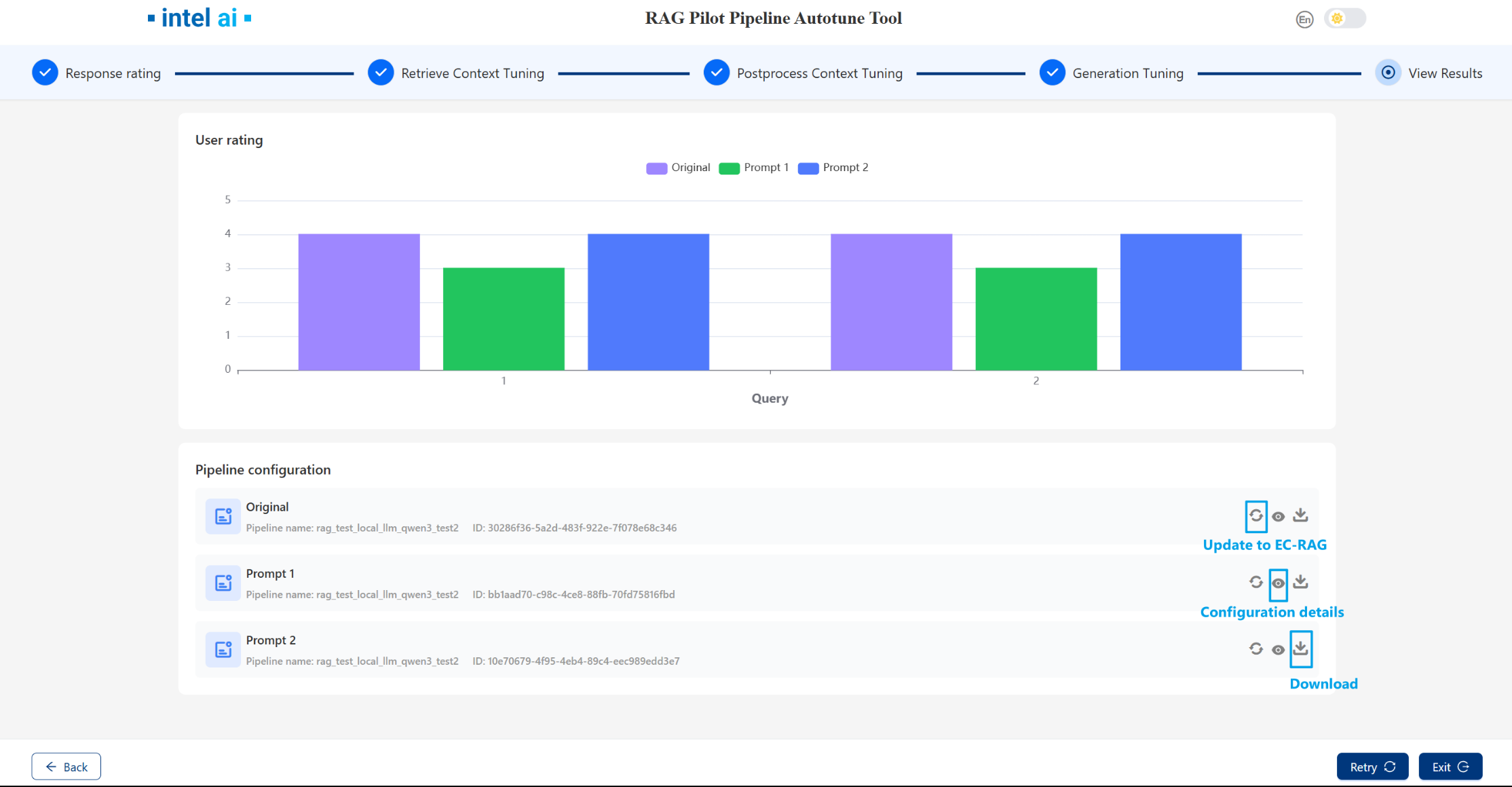
Note that once you run retrieval,postprocessing or generation stage , the EC-RAG active pipeline will be changed, you have to reset EC-RAG pipeline in EC-RAG server if needed.
▶️ Use RAG Pilot with RESTful API¶
Set EC-RAG endpoint¶
curl -X POST http://localhost:16030/v1/pilot/settings
-H 'Content-Type: application/json'
-d '{"target_endpoint": "10.67.106.189:16010","target_type":"ecrag"}'| jq '.'
Upload ground truth¶
curl -X POST http://localhost:16030/v1/pilot/ground_truth/file \
-H "Content-Type: multipart/form-data" \
-F "file=@{your ground truth csv path}" | jq '.'
Get current active pipeline¶
# get active pipeline id
curl -X GET http://localhost:16030/v1/pilot/pipeline/active/id | jq '.'
#get active pipeline detail configs
curl -X GET http://localhost:16030/v1/pilot/pipeline/active | jq '.'
Run current pipeline¶
curl -X POST http://localhost:16030/v1/pilot/pipeline/active/run| jq '.'
Get pipeline results¶
#get detail results
curl -X GET http://localhost:16030/v1/pilot/pipeline/{pipeline id}/results | jq '.'
#get pipeline metrics
curl -X GET http://localhost:16030/v1/pilot/pipeline/{pipeline id}/results/metrics | jq '.'
Run different stages¶
#stage including retrieval,postprocessing and generation
curl -X POST http://localhost:16030/v1/tuners/stage/{stage}/run | jq '.'
Get stage states¶
curl -X GET http://localhost:16030/v1/tuners/stage/{stage}/status | jq '.'
Get stage results¶
#get stage detail results
curl -X GET http://localhost:16030/v1/tuners/stage/{stage}/results | jq '.'
#get stage metrics
curl -X GET http://localhost:16030/v1/tuners/stage/{stage}/results/metrics | jq '.'
Get best stage pipeline¶
curl -X GET http://localhost:16030/v1/tuners/stage/{stage}/pipelines/best/id | jq '.'
Reset¶
Reset stage¶
curl -X POST http://localhost:16030/v1/tuners/stage/{stage}/reset | jq '.'
Note that once you run retrieval,postprocessing or generation stage , the EC-RAG active pipeline will be changed, you have to reset EC-RAG pipeline in EC-RAG server if needed.
🔧 How to Adjust RAG Pilot to Tune Your RAG Solution¶
🧩 What’s Nodes and Modules¶
RAG Pilot represents each stage of the RAG pipeline as a node, such as node_parser, indexer, retriever, etc. Each node can have different modules that define its type and configuration. The nodes and modules are specified in a YAML file, allowing user to switch between different implementations easily.
Here is an example of nodes and modules for EdgeCraftRAG.
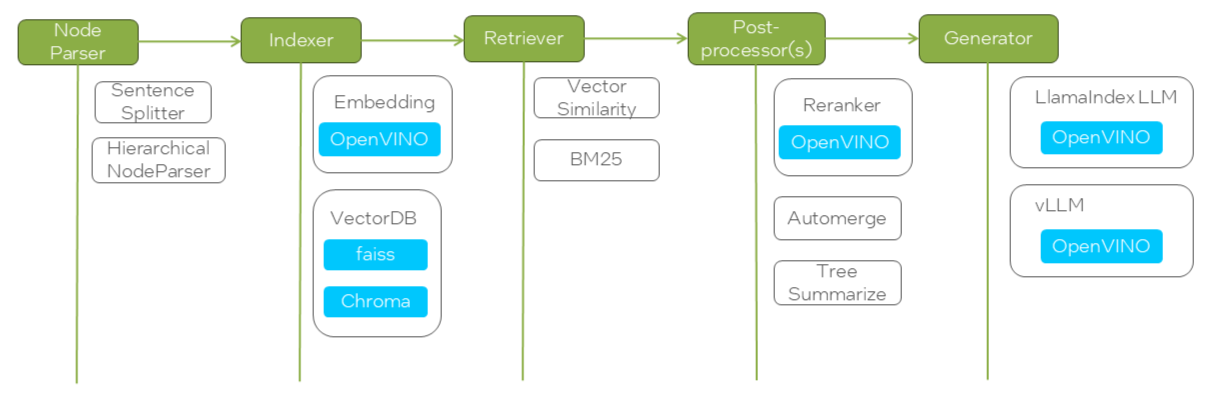
⚙️ How to Configure Nodes and Modules¶
The available nodes and their modules are stored in a YAML file (i.e. configs/ecrag.yaml for EdgeCraftRAG as below). Each node can have multiple modules, and both nodes and modules have configurable parameters that can be tuned.
nodes:
- node: node_parser
modules:
- module_type: simple
chunk_size: 400
chunk_overlap: 48
- module_type: hierarchical
chunk_sizes:
- 256
- 384
- 512
- node: indexer
embedding_model:
- BAAI/bge-small-zh-v1.5
- BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5
modules:
- module_type: vector
- module_type: faiss_vector
- node: retriever
retrieve_topk: 30
modules:
- module_type: vectorsimilarity
- module_type: auto_merge
- module_type: bm25
- node: postprocessor
modules:
- module_type: reranker
top_n: 3
reranker_model: BAAI/bge-reranker-large
- module_type: metadata_replace
- node: generator
model:
- Qwen/Qwen2-7B-Instruct
inference_type:
- local
- vllm
prompt: null
Each Node Can Have Multiple Modules
A node represents a stage in the RAG pipeline, such as
node_parser,indexer, orretriever.Each node can support different modules that define how it operates. For example, the
node_parsernode can use either asimpleorhierarchicalmodule.
Nodes Have Parameters to Tune
Some nodes have global parameters that affect all modules within them. For instance, the
retrievernode has aretrieve_topkparameter that defines how many top results are retrieved.
Modules Have Parameters to Tune
Each module within a node can have its own parameters. For example, the
simpleparser module haschunk_sizeandchunk_overlapparameters, while thehierarchicalparser module supports multiplechunk_sizes.
Each Node Selects Its Module Based on a Type Map
The tool uses an internal mapping to associate each module type with its corresponding function. The type of module selected for each node is defined in a mapping system like the one below:
COMP_TYPE_MAP = { "node_parser": "parser_type", "indexer": "indexer_type", "retriever": "retriever_type", "postprocessor": "processor_type", "generator": "inference_type", }
🧑💻 How to Use Nodes and Modules¶
Besides the YAML configuration file, the tool also uses a module map to associate each module with a runnable instance. This ensures that the tool correctly links each module type to its respective function within the pipeline.
🧾 Example: Mapping Modules to Functions¶
The function below defines how different module types are mapped to their respective components in EdgeCraftRAG:
def get_ecrag_module_map(ecrag_pl):
ecrag_modules = {
# root
"root": (ecrag_pl, ""),
# node_parser
"node_parser": (ecrag_pl, "node_parser"),
"simple": (ecrag_pl, "node_parser"),
"hierarchical": (ecrag_pl, "node_parser"),
"sentencewindow": (ecrag_pl, "node_parser"),
# indexer
"indexer": (ecrag_pl, "indexer"),
"vector": (ecrag_pl, "indexer"),
"faiss_vector": (ecrag_pl, "indexer"),
# retriever
"retriever": (ecrag_pl, "retriever"),
"vectorsimilarity": (ecrag_pl, "retriever"),
"auto_merge": (ecrag_pl, "retriever"),
"bm25": (ecrag_pl, "retriever"),
# postprocessor
"postprocessor": (ecrag_pl, "postprocessor[0]"),
"reranker": (ecrag_pl, "postprocessor[0]"),
"metadata_replace": (ecrag_pl, "postprocessor[0]"),
# generator
"generator": (ecrag_pl, "generator"),
}
return ecrag_modules
By modifying the YAML configuration file and understanding how modules are mapped to functions, you can experiment with different configurations and parameter settings to optimize their RAG pipeline effectively.