Document Summarization Application¶
Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized the way we interact with text. These models can be used to create summaries of news articles, research papers, technical documents, legal documents, multimedia documents, and other types of documents. Suppose you have a set of documents (PDFs, Notion pages, customer questions, multimedia files, etc.) and you want to summarize the content. In this example use case, we utilize LangChain to implement summarization strategies and facilitate LLM inference using Text Generation Inference.
Table of contents¶
Architecture¶
The architecture of the Document Summarization Application is illustrated below:
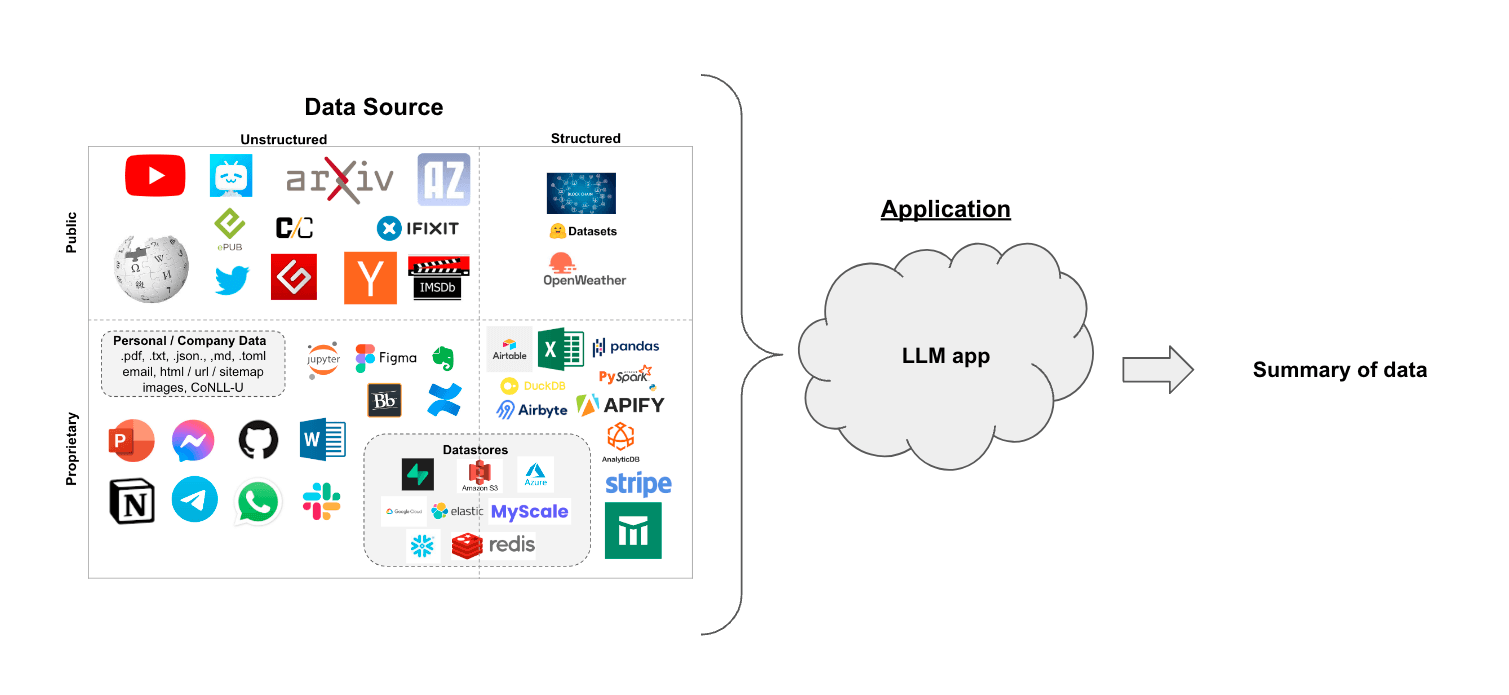
The DocSum example is implemented using the component-level microservices defined in GenAIComps. The flow chart below shows the information flow between different microservices for this example.
Deployment Options¶
The table below lists currently available deployment options. They outline in detail the implementation of this example on selected hardware.
Category |
Deployment Option |
Description |
|---|---|---|
On-premise Deployments |
Docker Compose (Xeon) |
|
Docker Compose (Gaudi) |
||
Docker Compose (EPYC) |
||
Docker Compose (ROCm) |
Validated Configurations¶
Deploy Method |
LLM Engine |
LLM Model |
Hardware |
|---|---|---|---|
Docker Compose |
vLLM, TGI |
meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct |
Intel Gaudi |
Docker Compose |
vLLM, TGI |
meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct |
Intel Xeon |
Docker Compose |
vLLM, TGI |
Intel/neural-chat-7b-v3-3 |
AMD EPYC |
Docker Compose |
vLLM, TGI |
Intel/neural-chat-7b-v3-3 |
AMD ROCm |
Helm Charts |
vLLM, TGI |
Intel/neural-chat-7b-v3-3 |
Intel Gaudi |
Helm Charts |
vLLM, TGI |
Intel/neural-chat-7b-v3-3 |
Intel Xeon |
Helm Charts |
vLLM, TGI |
Intel/neural-chat-7b-v3-3 |
AMD ROCm |