Deploying AgentQnA on Intel® Xeon® Processors¶
This document outlines the single node deployment process for a AgentQnA application utilizing the GenAIComps microservices on Intel Xeon server. The steps include pulling Docker images, container deployment via Docker Compose, and service execution using microservices agent.
Table of Contents¶
AgentQnA Quick Start Deployment¶
This section describes how to quickly deploy and test the AgentQnA service manually on an Intel® Xeon® processor. The basic steps are:
Access the Code¶
Clone the GenAIExample repository and access the AgentQnA Intel® Xeon® platform Docker Compose files and supporting scripts:
export WORKDIR=<your-work-directory>
cd $WORKDIR
git clone https://github.com/opea-project/GenAIExamples.git
cd GenAIExamples/AgentQnA
To checkout a released version, such as v1.4:
git checkout v1.4
Configure the Deployment Environment¶
To set up environment variables for deploying AgentQnA services, set up some parameters specific to the deployment environment and source the set_env.sh script in this directory:
export host_ip="External_Public_IP" # ip address of the node
export HF_TOKEN="Your_HuggingFace_API_Token" # the huggingface API token you applied
export http_proxy="Your_HTTP_Proxy" # http proxy if any
export https_proxy="Your_HTTPs_Proxy" # https proxy if any
export no_proxy=localhost,127.0.0.1,$host_ip # additional no proxies if needed
[Optional] OPENAI_API_KEY to use OpenAI models or LLM models with remote endpoints¶
To use OpenAI models, generate a key following these instructions.
When models are deployed on a remote server, a base URL and an API key are required to access them. To set up a remote server and acquire the base URL and API key, refer to Intel® AI for Enterprise Inference offerings.
Then set the environment variable OPENAI_API_KEY with the key contents:
export OPENAI_API_KEY=<your-openai-key>
Then, set up environment variables for the selected hardware using the corresponding set_env.sh¶
cd $WORKDIR/GenAIExamples/AgentQnA/docker_compose/intel/cpu/xeon
source ./set_env.sh
Deploy the Services Using Docker Compose¶
We make it convenient to launch the whole system with docker compose, which includes microservices for LLM, agents, UI, retrieval tool, vector database, dataprep, and telemetry. There are 3 docker compose files, which make it easy for users to pick and choose. Users can choose a different retrieval tool other than the DocIndexRetriever example provided in our GenAIExamples repo. Users can choose not to launch the telemetry containers.
On Xeon, OpenAI models and models deployed on a remote server are supported. Both methods require an API key where OPENAI_API_KEY needs to be set in the previous step.
cd $WORKDIR/GenAIExamples/AgentQnA/docker_compose/intel/cpu/xeon
OpenAI Models¶
The command below will launch the multi-agent system with the DocIndexRetriever as the retrieval tool for the Worker RAG agent.
docker compose -f $WORKDIR/GenAIExamples/DocIndexRetriever/docker_compose/intel/cpu/xeon/compose.yaml -f compose_openai.yaml up -d
Models on Remote Servers¶
When models are deployed on a remote server with Intel® AI for Enterprise Inference, a base URL and an API key are required to access them. To run the Agent microservice on Xeon while using models deployed on a remote server, add compose_remote.yaml to the docker compose command and set additional environment variables.
Note: For AgentQnA, the minimum hardware requirement for the remote server is Intel® Gaudi® AI Accelerators.
Set the following environment variables.
REMOTE_ENDPOINTis the HTTPS endpoint of the remote server with the model of choice (i.e. https://api.example.com). Note: If the API for the models does not use LiteLLM, the second part of the model card needs to be appended to the URL. For example, setREMOTE_ENDPOINTto https://api.example.com/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct if the model card ismeta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct.modelis the model card which may need to be overwritten depending on what it is set toset_env.sh.
export REMOTE_ENDPOINT=<https-endpoint-of-remote-server>
export model=<model-card>
After setting these environment variables, run docker compose by adding compose_remote.yaml as an additional YAML file:
docker compose -f $WORKDIR/GenAIExamples/DocIndexRetriever/docker_compose/intel/cpu/xeon/compose.yaml -f compose_openai.yaml -f compose_remote.yaml up -d
Build image from source¶
Please refer to the table below to build different microservices from source:
Microservice |
Deployment Guide |
|---|---|
Agent |
|
UI |
Ingest Data into the Vector Database¶
The run_ingest_data.sh script will use an example jsonl file to ingest example documents into a vector database. Other ways to ingest data and other types of documents supported can be found in the OPEA dataprep microservice located in the opea-project/GenAIComps repo.
cd $WORKDIR/GenAIExamples/AgentQnA/retrieval_tool/
bash run_ingest_data.sh
Note: This is a one-time operation.
Cleanup the Deployment¶
To stop the containers associated with the deployment, execute the following command:
# for OpenAI Models
docker compose -f compose_openai.yaml down
# for Models on Remote Server
docker compose -f compose_remote.yaml down
Configuration Parameters¶
Key parameters are configured via environment variables set before running docker compose up.
Environment Variable |
Description |
Default (Set Externally) |
|---|---|---|
|
External IP address of the host machine. Required. |
|
|
Your OpenAI API key for model access. Required. |
|
|
Hugging Face model ID for the AgentQnA LLM. Configured within |
|
|
Local path to the tool Yaml file. Configured in |
|
|
CRAG server URL. Derived from |
|
|
Worker agent URL. Derived from |
|
|
SQL agent URL. Derived from |
|
|
Network proxy settings (if required). |
|
AgentQnA Docker Compose Files¶
In the context of deploying a AgentQnA pipeline on an Intel® Xeon® platform, we can pick and choose different large language model serving frameworks. The table below outlines the various configurations that are available as part of the application. These configurations can be used as templates and can be extended to different components available in GenAIComps.
File |
Description |
|---|---|
Default compose file using OpenAI-compatible API as the serving framework |
|
This compose file is used to connect to a remote LLM service (such as a self-hosted or third-party API). All other configurations remain the same as the default. |
Validate Services¶
First look at logs for each of the agent docker containers:
# worker RAG agent
docker logs rag-agent-endpoint
# worker SQL agent
docker logs sql-agent-endpoint
# supervisor agent
docker logs react-agent-endpoint
Look for the message “HTTP server setup successful” to confirm the agent docker container has started successfully.
Use python to validate each agent is working properly:
# RAG worker agent
python $WORKDIR/GenAIExamples/AgentQnA/tests/test.py --prompt "Tell me about Michael Jackson song Thriller" --agent_role "worker" --ext_port 9095
# SQL agent
python $WORKDIR/GenAIExamples/AgentQnA/tests/test.py --prompt "How many employees in company" --agent_role "worker" --ext_port 9096
# supervisor agent: this will test a two-turn conversation
python $WORKDIR/GenAIExamples/AgentQnA/tests/test.py --agent_role "supervisor" --ext_port 9090
Interact with the agent system with UI¶
The UI microservice is launched in the previous step with the other microservices.
To see the UI, open a web browser to http://${ip_address}:5173 to access the UI. Note the ip_address here is the host IP of the UI microservice.
Click on the arrow above
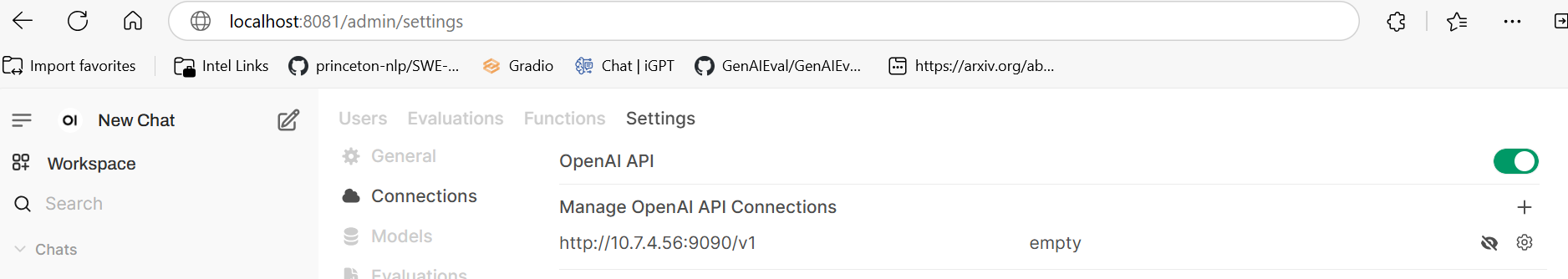
Get started. Create an admin account with a name, email, and password.Add an OpenAI-compatible API endpoint. In the upper right, click on the circle button with the user’s initial, go to
Admin Settings->Connections. UnderManage OpenAI API Connections, click on the+to add a connection. Fill in these fields:
URL:
http://${ip_address}:9090/v1, do not forget thev1Key: any value
Model IDs: any name i.e.
opea-agent, then press+to add it
Click “Save”.
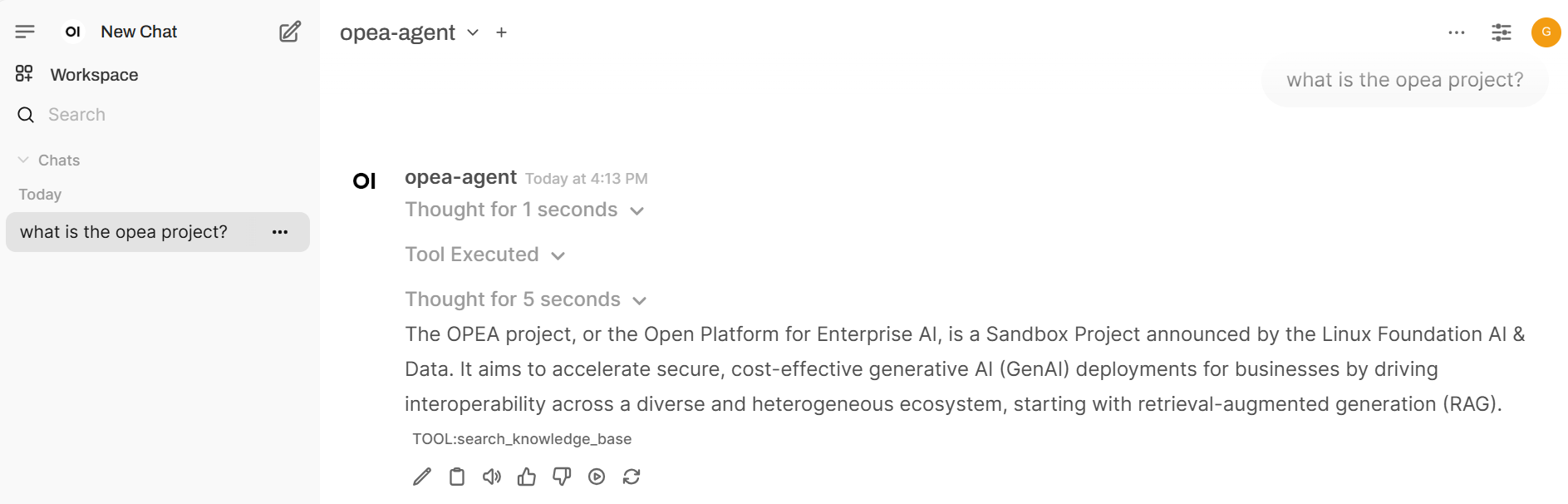
Test OPEA agent with UI. Return to
New Chatand ensure the model (i.e.opea-agent) is selected near the upper left. Enter in any prompt to interact with the agent.
Register other tools with the AI agent¶
The tools folder contains YAML and Python files for additional tools for the supervisor and worker agents. Refer to the “Provide your own tools” section in the instructions here to add tools and customize the AI agents.
Conclusion¶
This guide provides a comprehensive workflow for deploying, configuring, and validating the AgentQnA system on Intel® Xeon® processors, enabling flexible integration with both OpenAI-compatible and remote LLM services.