Agents for Question and Answering Application¶
AI agents bring unique advantages to question-answering tasks, as demonstrated in the AgentQnA application:
Improve relevancy of retrieved context. RAG agents can rephrase user queries, decompose user queries, and iterate to get the most relevant context for answering a user’s question. Compared to conventional RAG, RAG agents significantly improve the correctness and relevancy of the answer because of the iterations it goes through.
Expand scope of skills. The supervisor agent interacts with multiple worker agents that specialize in different skills (e.g., retrieve documents, write SQL queries, etc.). Thus, it can answer questions with different methods.
Hierarchical multi-agents improve performance. Expert worker agents, such as RAG agents and SQL agents, can provide high-quality output for different aspects of a complex query, and the supervisor agent can aggregate the information to provide a comprehensive answer. If only one agent is used and all tools are provided to this single agent, it can lead to large overhead or not use the best tool to provide accurate answers.
Table of contents¶
Architecture¶
This example showcases a hierarchical multi-agent system for question-answering applications. The architecture diagram below shows a supervisor agent that interfaces with the user and dispatches tasks to two worker agents to gather information and come up with answers. The worker RAG agent uses the retrieval tool to retrieve relevant documents from a knowledge base - a vector database. The worker SQL agent retrieves relevant data from a SQL database. Although not included in this example by default, other tools such as a web search tool or a knowledge graph query tool can be used by the supervisor agent to gather information from additional sources.
The AgentQnA application is an end-to-end workflow that leverages the capability of agents and tools. The workflow falls into the following architecture:
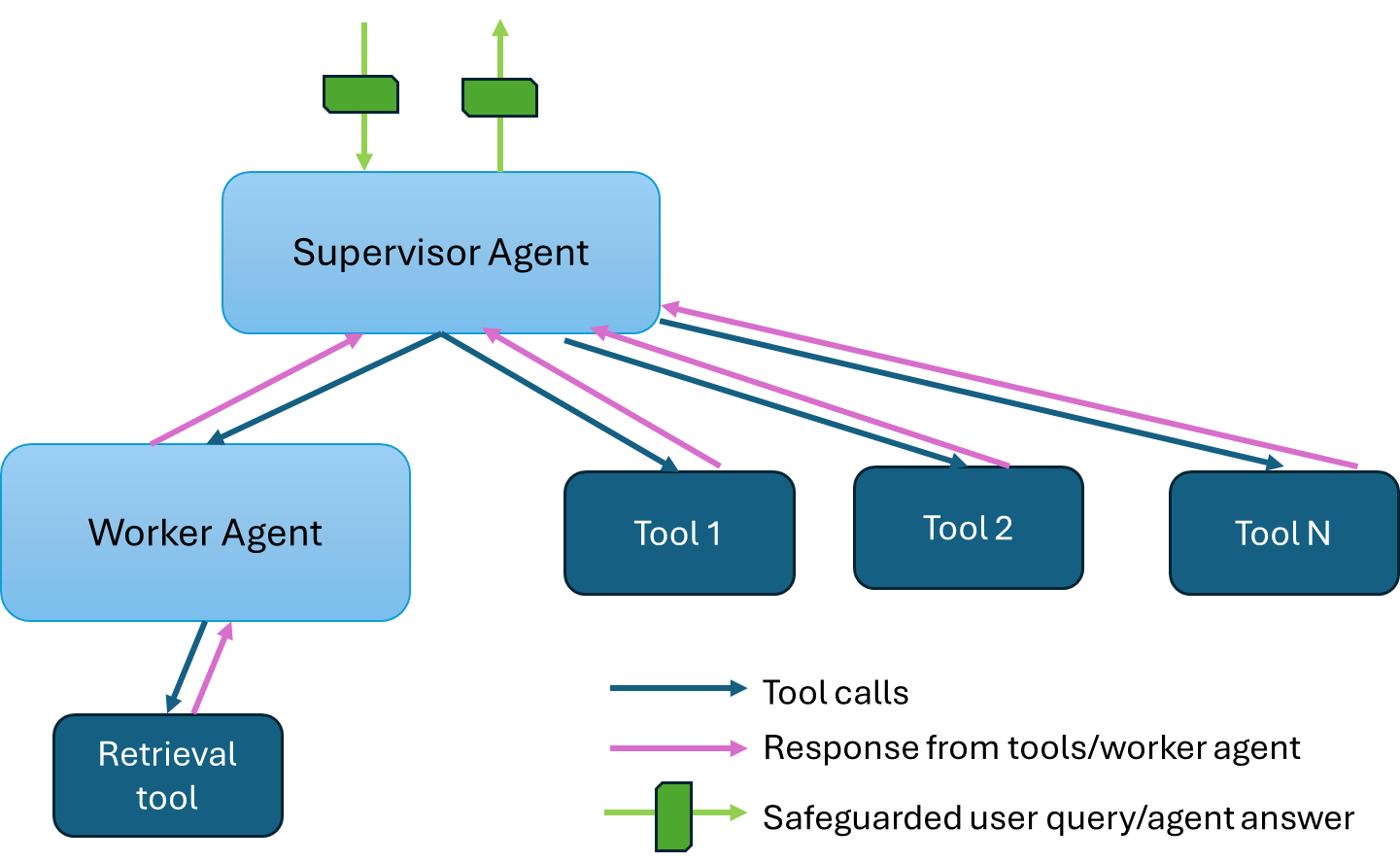
The AgentQnA example is implemented using the component-level microservices defined in GenAIComps.
Deployment Options¶
The table below lists currently available deployment options. They outline in detail the implementation of this example on selected hardware.
Category |
Deployment Option |
Description |
|---|---|---|
On-premise Deployments |
Docker compose |
|
Kubernetes |
||
Azure |
Work-in-progress |
|
Intel Tiber AI Cloud |
Work-in-progress |
Validated Configurations¶
Deploy Method |
LLM Engine |
LLM Model |
Hardware |
|---|---|---|---|
Docker Compose |
vLLM |
meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct |
Intel Gaudi |
Docker Compose |
vLLM, TGI |
Intel/neural-chat-7b-v3-3 |
AMD ROCm |
Helm Charts |
vLLM |
meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct |
Intel Gaudi |
Helm Charts |
vLLM |
meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct |
Intel Xeon |