Codegen Sample Guide¶
Note
This guide is in its early development and is a work-in-progress with placeholder content.
Overview¶
The CodeGen example uses specialized AI models that went through training with datasets that encompass repositories, documentation, programming code, and web data. With an understanding of various programming languages, coding patterns, and software development concepts, the CodeGen LLMs assist developers and programmers. The LLMs can be integrated into the developers’ Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) to have more contextual awareness to write more refined and relevant code based on the suggestions.
Purpose¶
Code Generation: Streamline coding through Code Generation, enabling non-programmers to describe tasks for code creation.
Code Completion: Accelerate coding by suggesting contextually relevant snippets as developers type.
Code Translation and Modernization: Translate and modernize code across multiple programming languages, aiding interoperability and updating legacy projects.
Code Summarization: Extract key insights from codebases, improving readability and developer productivity.
Code Refactoring: Offer suggestions for code refactoring, enhancing code performance and efficiency.
AI-Assisted Testing: Assist in creating test cases, ensuring code robustness and accelerating development cycles.
Error Detection and Debugging: Detect errors in code and provide detailed descriptions and potential fixes, expediting debugging processes.
How It Works¶
The CodeGen example uses an open-source code generation model with Text Generation Inference (TGI) for serving deployment. It is presented as a Code Copilot application as shown in the diagram below.
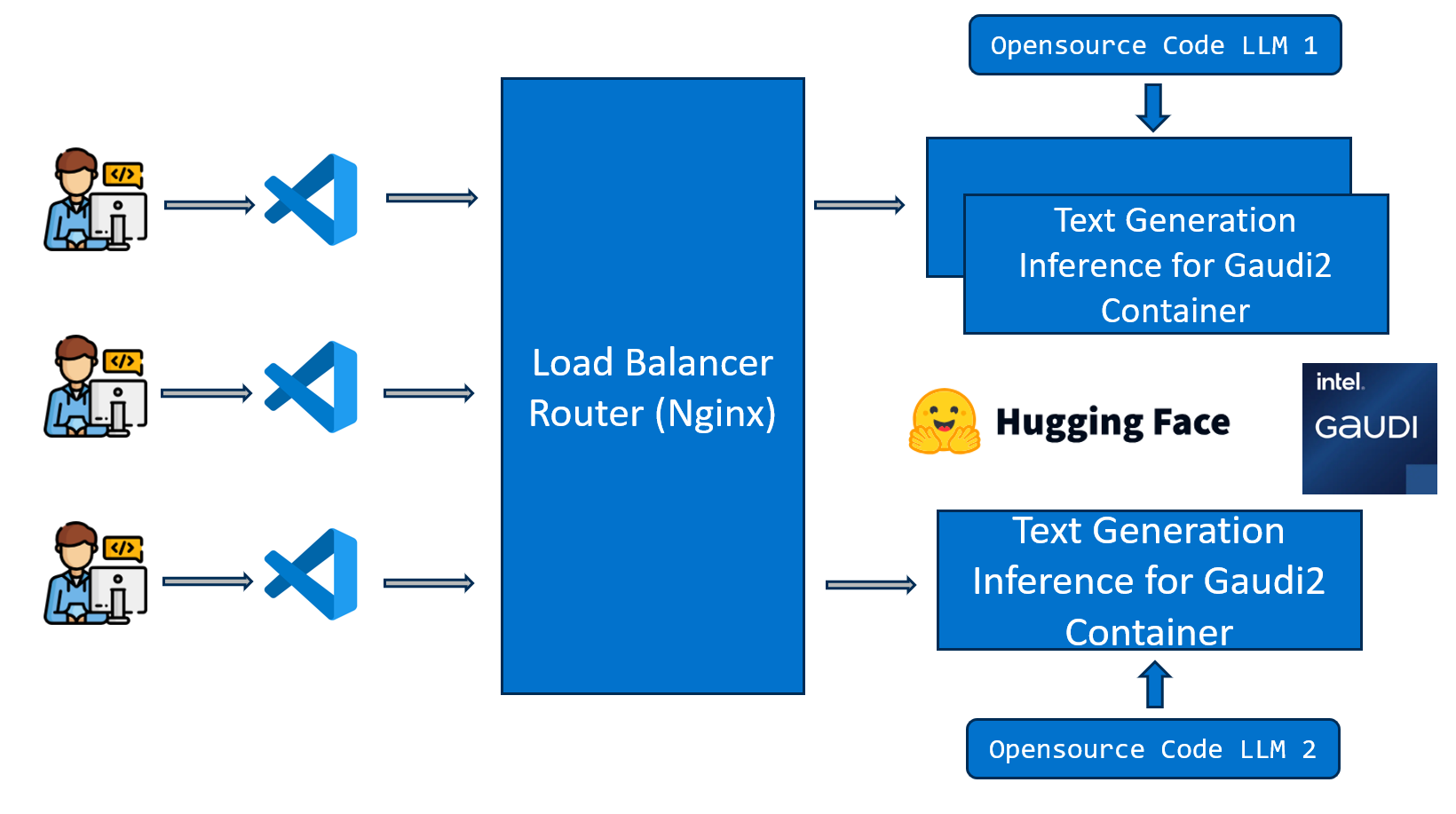
Deployment¶
Here are some deployment options, depending on your hardware and environment: