Code Generation Application¶
Code Generation (CodeGen) Large Language Models (LLMs) are specialized AI models designed for the task of generating computer code. Such models undergo training with datasets that encompass repositories, specialized documentation, programming code, relevant web content, and other related data. They possess a deep understanding of various programming languages, coding patterns, and software development concepts. CodeGen LLMs are engineered to assist developers and programmers. When these LLMs are seamlessly integrated into the developer’s Integrated Development Environment (IDE), they possess a comprehensive understanding of the coding context, which includes elements such as comments, function names, and variable names. This contextual awareness empowers them to provide more refined and contextually relevant coding suggestions.
The capabilities of CodeGen LLMs include:
Code Generation: Streamline coding through Code Generation, enabling non-programmers to describe tasks for code creation.
Code Completion: Accelerate coding by suggesting contextually relevant snippets as developers type.
Code Translation and Modernization: Translate and modernize code across multiple programming languages, aiding interoperability and updating legacy projects.
Code Summarization: Extract key insights from codebases, improving readability and developer productivity.
Code Refactoring: Offer suggestions for code refactoring, enhancing code performance and efficiency.
AI-Assisted Testing: Assist in creating test cases, ensuring code robustness and accelerating development cycles.
Error Detection and Debugging: Detect errors in code and provide detailed descriptions and potential fixes, expediting debugging processes.
In this example, we present a Code Copilot application to showcase how code generation can be executed on either Intel Gaudi2 platform or Intel Xeon Processor platform. This CodeGen use case involves code generation utilizing open-source models such as m-a-p/OpenCodeInterpreter-DS-6.7B and deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-33b-instruct with Text Generation Inference (TGI) for serving deployment.
The workflow falls into the following architecture:
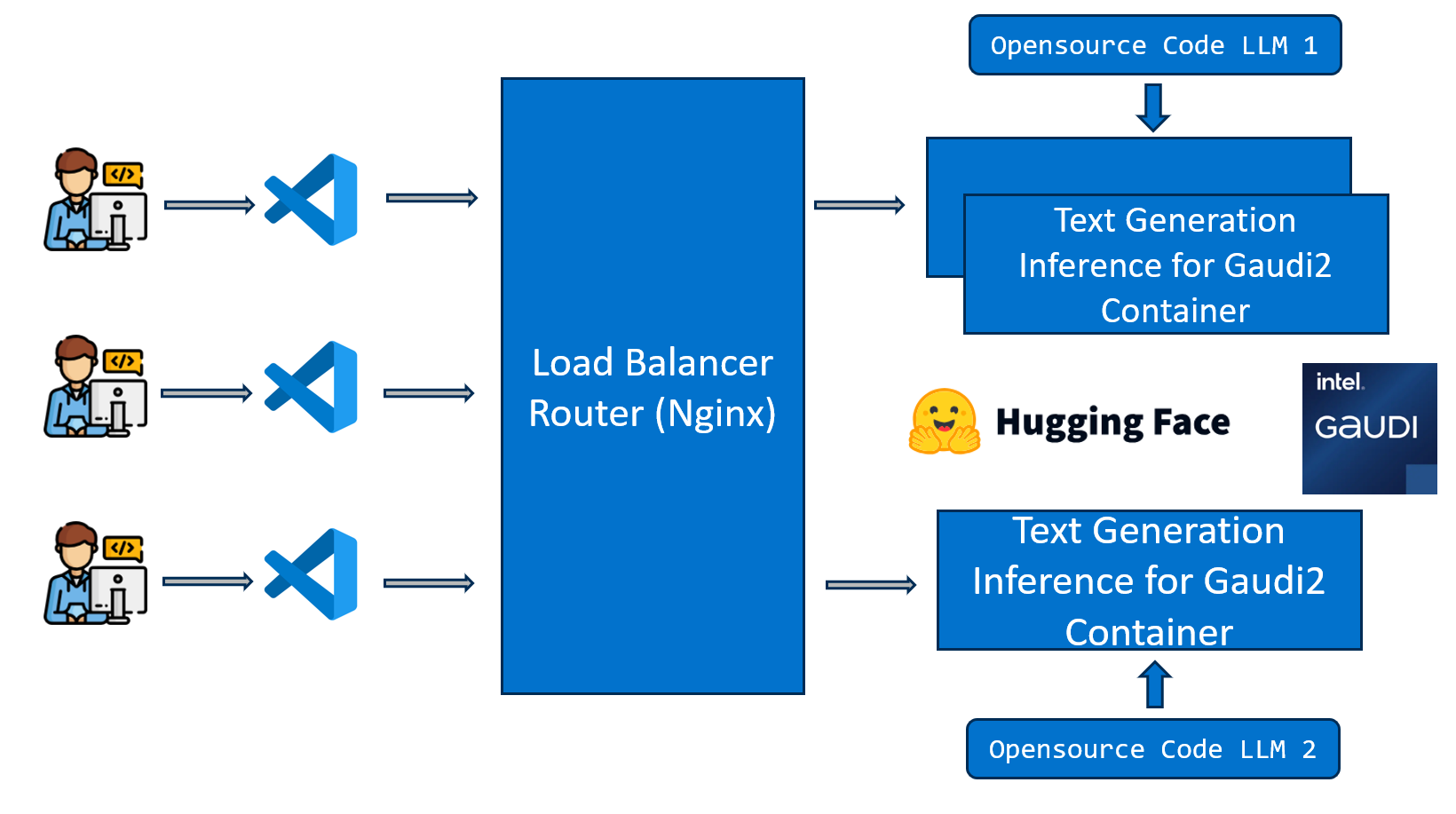
The CodeGen example is implemented using the component-level microservices defined in GenAIComps. The flow chart below shows the information flow between different microservices for this example.
Deploy CodeGen Service¶
The CodeGen service can be effortlessly deployed on either Intel Gaudi2 or Intel Xeon Scalable Processor.
Currently we support two ways of deploying ChatQnA services with docker compose:
Start services using the docker image on
docker hub:docker pull opea/codegen:latest
Start services using the docker images built from source. See the Gaudi Guide or Xeon Guide for more information.
Required Models¶
By default, the LLM model is set to a default value as listed below:
Service |
Model |
|---|---|
LLM_MODEL_ID |
Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-7B-Instruct may be a gated model that requires submitting an access request through Hugging Face. You can replace it with another model.
Change the LLM_MODEL_ID below for your needs, such as: deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-instruct
If you choose to use meta-llama/CodeLlama-7b-hf as LLM model, you will need to visit here, click the Expand to review and access button to ask for model access.
Setup Environment Variable¶
To set up environment variables for deploying ChatQnA services, follow these steps:
Set the required environment variables:
# Example: host_ip="192.168.1.1" export host_ip="External_Public_IP" # Example: no_proxy="localhost, 127.0.0.1, 192.168.1.1" export no_proxy="Your_No_Proxy" export HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN="Your_Huggingface_API_Token"
If you are in a proxy environment, also set the proxy-related environment variables:
export http_proxy="Your_HTTP_Proxy" export https_proxy="Your_HTTPs_Proxy"
Set up other environment variables:
source ./docker_compose/set_env.sh
Deploy CodeGen using Docker¶
Deploy CodeGen on Gaudi¶
Find the corresponding compose.yaml.
cd GenAIExamples/CodeGen/docker_compose/intel/hpu/gaudi
docker compose up -d
Refer to the Gaudi Guide to build docker images from source.
Deploy CodeGen on Xeon¶
Find the corresponding compose.yaml.
cd GenAIExamples/CodeGen/docker_compose/intel/cpu/xeon
docker compose up -d
Refer to the Xeon Guide for more instructions on building docker images from source.
Deploy CodeGen using Kubernetes¶
Refer to the Kubernetes Guide for instructions on deploying CodeGen into Kubernetes on Xeon & Gaudi.
Deploy CodeGen into Kubernetes using Helm Chart¶
Install Helm (version >= 3.15) first. Refer to the Helm Installation Guide for more information.
Refer to the CodeGen helm chart for instructions on deploying CodeGen into Kubernetes on Xeon & Gaudi.
Consume CodeGen Service¶
Two ways of consuming CodeGen Service:
Use cURL command on terminal
curl http://${host_ip}:7778/v1/codegen \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{"messages": "Implement a high-level API for a TODO list application. The API takes as input an operation request and updates the TODO list in place. If the request is invalid, raise an exception."}'
Access via frontend
To access the frontend, open the following URL in your browser: http://{host_ip}:5173.
By default, the UI runs on port 5173 internally.
Troubleshooting¶
If you get errors like “Access Denied”, validate micro service first. A simple example:
http_proxy="" curl http://${host_ip}:8028/generate \ -X POST \ -d '{"inputs":"Implement a high-level API for a TODO list application. The API takes as input an operation request and updates the TODO list in place. If the request is invalid, raise an exception.","parameters":{"max_tokens":256, "do_sample": true}}' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json'
If you get errors like “aiohttp.client_exceptions.ClientConnectorError: Cannot connect to host xx.xx.xx.xx:8028”, check the
tgi servicefirst. If there is “Cannot access gated repo for url https://huggingface.co/meta-llama/CodeLlama-7b-hf/resolve/main/config.json.” error oftgi service, Then you need to ask for model access first. Follow the instruction in the Required Models section for more information.(Docker only) If all microservices work well, check the port ${host_ip}:7778, the port may be allocated by other users, you can modify the
compose.yaml.(Docker only) If you get errors like “The container name is in use”, change container name in
compose.yaml.