🚀 RAG Pilot - A RAG Pipeline Tuning Tool¶
📖 Overview¶
RAG Pilot provides a set of tuners to optimize various parameters in a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) pipeline. Each tuner allows fine-grained control over key aspects of parsing, chunking, postporcessing, and generating selection, enabling better retrieval and response generation.
🧠 Available Tuners¶
Tuner |
Stage |
Function |
Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|
EmbeddingTuner |
Retrieval |
Tune embedding model and related parameters |
Allows selection and configuration of the embedding model used for vectorization, including model name and optional parameters like dimension or backend. |
NodeParserTuner |
Retrieval |
Tune node parser parameters |
General tuner for configuring node parsers, possibly extending to custom strategies or pre-processing logic. |
SimpleNodeParserChunkTuner |
Retrieval |
Tune |
Configures chunking behavior for document parsing by adjusting the size of individual text chunks and their overlap to ensure context retention. |
RetrievalTopkTuner |
Retrieval |
Tune |
Adjusts how many documents are retrieved before reranking, balancing recall and performance. |
RerankerTopnTuner |
Postprocessing |
Tune |
Adjusts the number of top-ranked documents returned after reranking, optimizing relevance and conciseness. |
These tuners help in optimizing document parsing, chunking strategies, reranking efficiency, and embedding selection for improved RAG performance.
🌐 Online RAG Tuning¶
⚙️ Dependencies and Environment Setup¶
🛠️ Setup EdgeCraftRAG¶
Setup EdgeCraftRAG pipeline based on this link.
Load documents in EdgeCraftRAG before running RAG Pilot.
🧪 Create Running Environment¶
# Create a virtual environment
python3 -m venv rag_pilot
source rag_pilot/bin/activate
# Install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
🚦 Launch RAG Pilot in Online Mode¶
To launch RAG Pilot, create the following required files before running the command:
🔹Input file: QA List File (your_queries.csv)¶
The input CSV file should contain queries and associated ground truth data (optional) used for evaluation or tuning. Each row corresponds to a specific query and context file. The CSV must include the following columns:
Column |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
✅ Yes |
Unique identifier for the query. Can be used to group multiple context entries under the same query. |
|
✅ Yes (at least one per |
The actual query string. If left empty for some rows sharing the same |
|
✅ Yes |
The name of the file or document where the context (for retrieval or grounding) is drawn from. |
|
✅ Yes |
The ground truth context string that should be retrieved or matched against. |
|
❌ Optional |
The ideal answer or response for the query, used for optional answer-level evaluation. |
📌 CSV File Example¶
query_id,query,file_name,gt_context,ground_truth
53,故障来源有哪些?,故障处理记录表.txt,故障来源:用户投诉、日志系统、例行维护中发现、其它来源。,故障来源:用户投诉、日志系统、例行维护中发现、其它来源。
93,uMAC网元VNFC有哪几种备份方式,index.txt,ZUF-76-04-005 VNFC支持1+1主备冗余,uMAC网元VFNC有3中备份方式: 支持1+1主备冗余,支持N+M负荷分担冗余, 支持1+1互备冗余。
93,,index.txt,ZUF-76-04-006 VNFC支持N+M负荷分担冗余,
93,,index.txt,ZUF-76-04-008 VNFC支持1+1互备冗余,
▶️ Run RAG Pilot¶
Run the following command to start the tuning process.
# Run pipeline tuning tool
export ECRAG_SERVICE_HOST_IP="ecrag_host_ip"
python3 -m run_pilot -q "your_queries.csv"
📦 Output Files and Structure¶
Each tuning run in RAG Pilot generates a set of structured output files for analyzing and comparing different RAG pipeline configurations.
📁 Directory Layout¶
rag_pilot_<timestamp>/: Main folder for a tuning session.curr_pipeline.json– Best pipeline configuration.curr_rag_results.json– Results of the best pipeline.rag_summary.csv– Query-wise summary.rag_contexts.csv– Detailed context analysis.summary.csv– Overall performance metrics.entry_<hash>/: Subfolders for each tried pipeline with the same file structure:pipeline.jsonrag_results.jsonrag_summary.csvrag_contexts.csv
🗂️ Output File Overview¶
File Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
RAG pipeline configuration used in a specific trial |
|
List of results for each query, including metadata and context sets |
|
Summary of each query’s outcome, including response and context hit counts |
|
Breakdown of retrieved/reranked contexts and mapping to ground truth |
|
Aggregated performance summary across all queries |
Context Mapping Notes:
Contexts are categorized as
gt_contexts,retrieval_contexts, orpostprocessing_contexts.Mappings track which retrieved or postprocessed contexts hit the ground truth.
Each context is associated with a
query_idand indexed for traceability.
📴 Offline RAG Tuning¶
RAG Pilot supports offline mode using a RAG configuration file.
⚙️ Environment Setup¶
Refer to Create Running Environment in the Online RAG pipeline tuning section for setting up the environment before proceeding.
🚦 Launch RAG Pilot in Offline Mode¶
To be added in later release
🔧 How to Adjust RAG Pilot to Tune Your RAG Solution¶
🧩 What’s Nodes and Modules¶
RAG Pilot represents each stage of the RAG pipeline as a node, such as node_parser, indexer, retriever, etc. Each node can have different modules that define its type and configuration. The nodes and modules are specified in a YAML file, allowing users to switch between different implementations easily.
Here is an example of nodes and modules for EdgeCraftRAG.
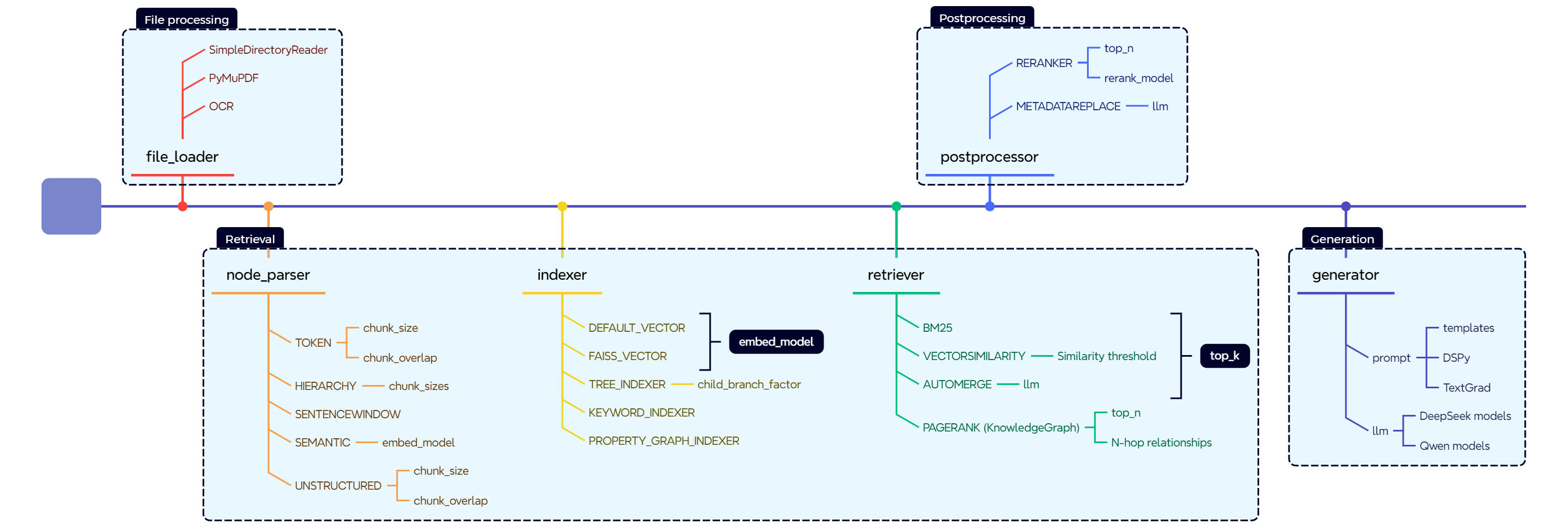
⚙️ How to Configure Nodes and Modules¶
The available nodes and their modules are stored in a YAML file (i.e. configs/ecrag.yaml for EdgeCraftRAG as below). Each node can have multiple modules, and both nodes and modules have configurable parameters that can be tuned.
nodes:
- node: node_parser
modules:
- module_type: simple
chunk_size: 400
chunk_overlap: 48
- module_type: hierarchical
chunk_sizes:
- 256
- 384
- 512
- node: indexer
embedding_model:
- BAAI/bge-small-zh-v1.5
- BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5
modules:
- module_type: vector
- module_type: faiss_vector
- node: retriever
retrieve_topk: 30
modules:
- module_type: vectorsimilarity
- module_type: auto_merge
- module_type: bm25
- node: postprocessor
modules:
- module_type: reranker
top_n: 3
reranker_model: BAAI/bge-reranker-large
- module_type: metadata_replace
- node: generator
model:
- Qwen/Qwen2-7B-Instruct
inference_type:
- local
- vllm
prompt: null
Each Node Can Have Multiple Modules
A node represents a stage in the RAG pipeline, such as
node_parser,indexer, orretriever.Each node can support different modules that define how it operates. For example, the
node_parsernode can use either asimpleorhierarchicalmodule.
Nodes Have Parameters to Tune
Some nodes have global parameters that affect all modules within them. For instance, the
retrievernode has aretrieve_topkparameter that defines how many top results are retrieved.
Modules Have Parameters to Tune
Each module within a node can have its own parameters. For example, the
simpleparser module haschunk_sizeandchunk_overlapparameters, while thehierarchicalparser module supports multiplechunk_sizes.
Each Node Selects Its Module Based on a Type Map
The tool uses an internal mapping to associate each module type with its corresponding function. The type of module selected for each node is defined in a mapping system like the one below:
COMP_TYPE_MAP = { "node_parser": "parser_type", "indexer": "indexer_type", "retriever": "retriever_type", "postprocessor": "processor_type", "generator": "inference_type", }
🧑💻 How to Use Nodes and Modules¶
Besides the YAML configuration file, the tool also uses a module map to associate each module with a runnable instance. This ensures that the tool correctly links each module type to its respective function within the pipeline.
🧾 Example: Mapping Modules to Functions¶
The function below defines how different module types are mapped to their respective components in EdgeCraftRAG:
def get_ecrag_module_map(ecrag_pl):
ecrag_modules = {
# root
"root": (ecrag_pl, ""),
# node_parser
"node_parser": (ecrag_pl, "node_parser"),
"simple": (ecrag_pl, "node_parser"),
"hierarchical": (ecrag_pl, "node_parser"),
"sentencewindow": (ecrag_pl, "node_parser"),
# indexer
"indexer": (ecrag_pl, "indexer"),
"vector": (ecrag_pl, "indexer"),
"faiss_vector": (ecrag_pl, "indexer"),
# retriever
"retriever": (ecrag_pl, "retriever"),
"vectorsimilarity": (ecrag_pl, "retriever"),
"auto_merge": (ecrag_pl, "retriever"),
"bm25": (ecrag_pl, "retriever"),
# postprocessor
"postprocessor": (ecrag_pl, "postprocessor[0]"),
"reranker": (ecrag_pl, "postprocessor[0]"),
"metadata_replace": (ecrag_pl, "postprocessor[0]"),
# generator
"generator": (ecrag_pl, "generator"),
}
return ecrag_modules
By modifying the YAML configuration file and understanding how modules are mapped to functions, you can experiment with different configurations and parameter settings to optimize their RAG pipeline effectively.